Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Practice Questions
Table of Contents
These practice questions will test you on your understanding of the reactions (and reactivity) of carboxylic acid derivatives, as well as their mechanisms.
Quiz count: 75
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip

Rank reactivity
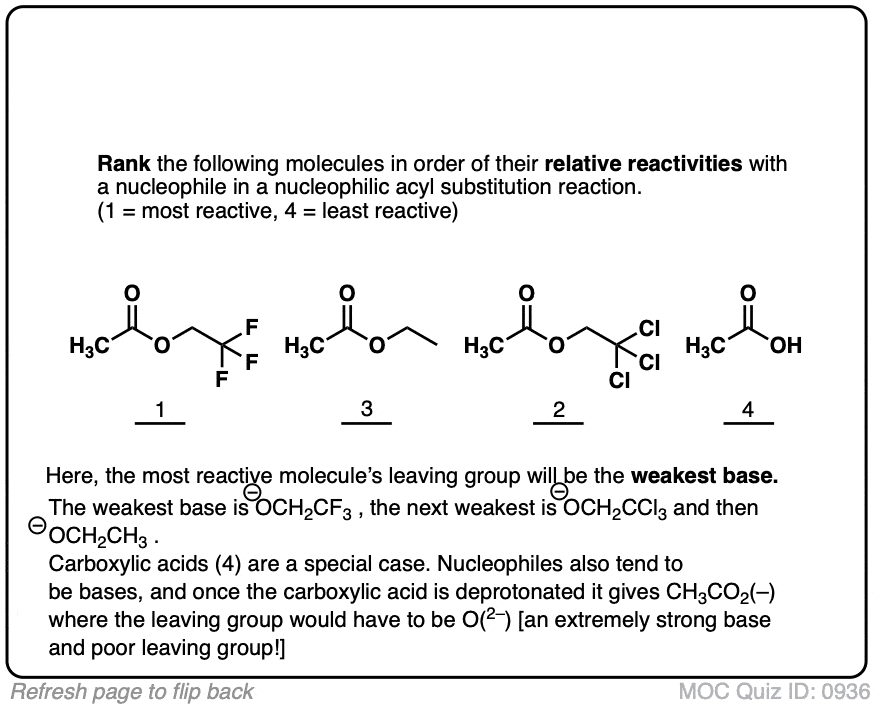
Quiz#: 936
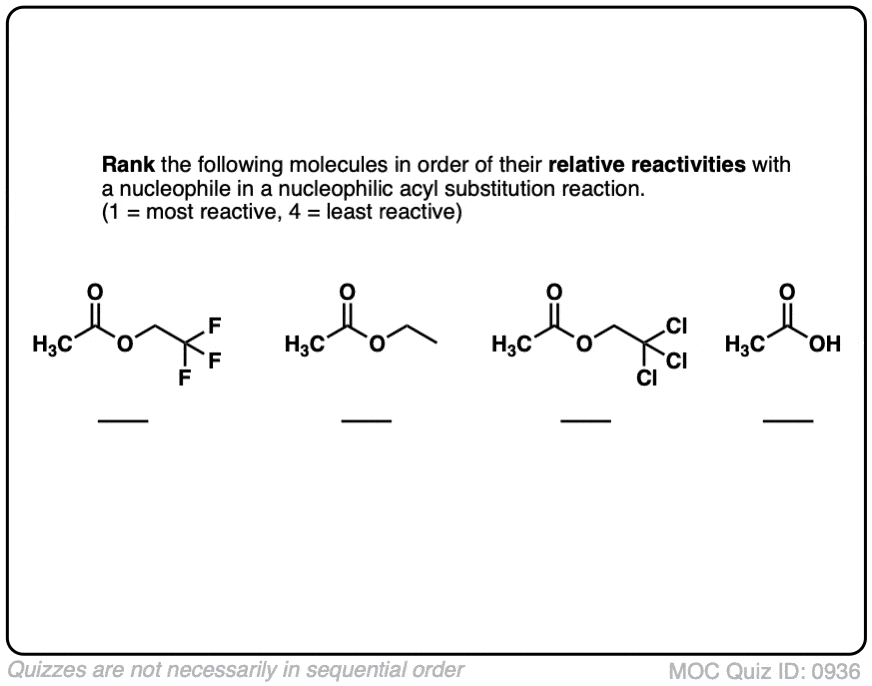 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
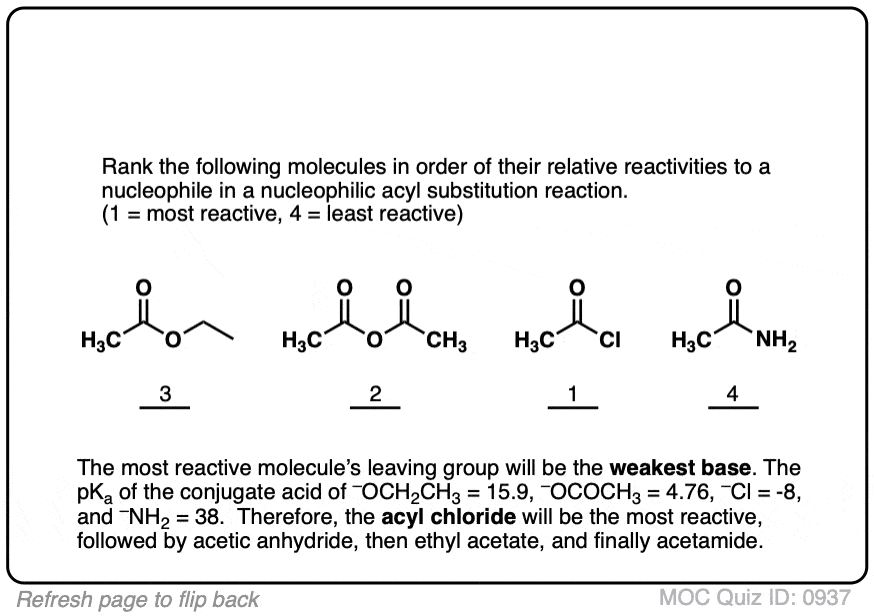
Quiz#: 937
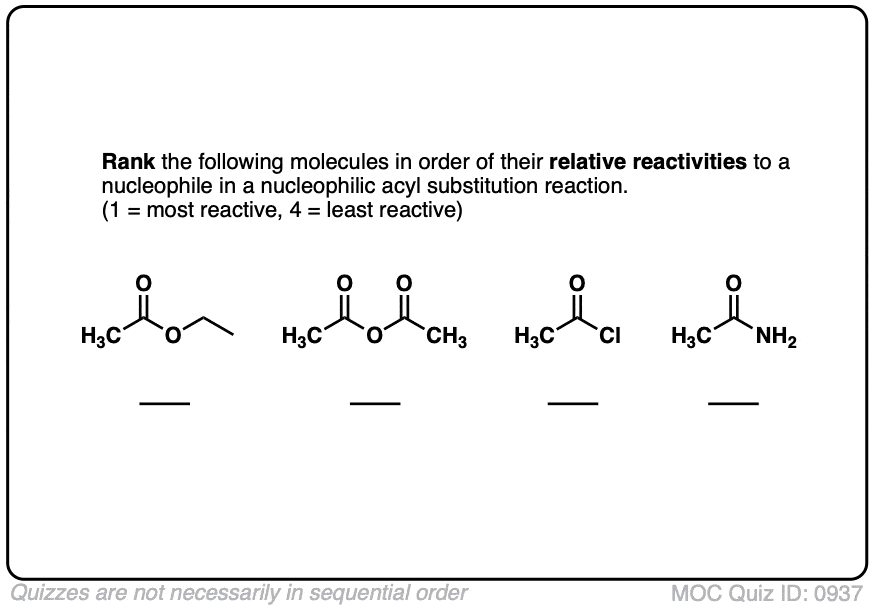 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
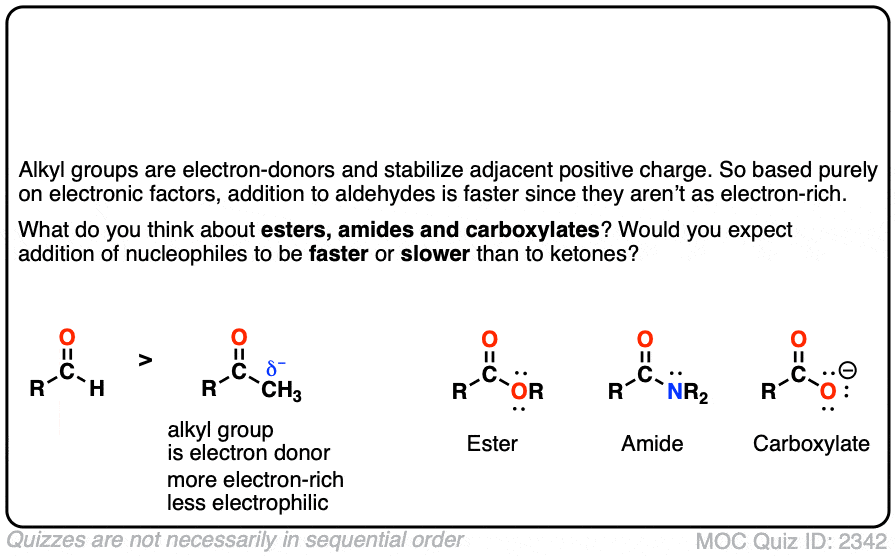
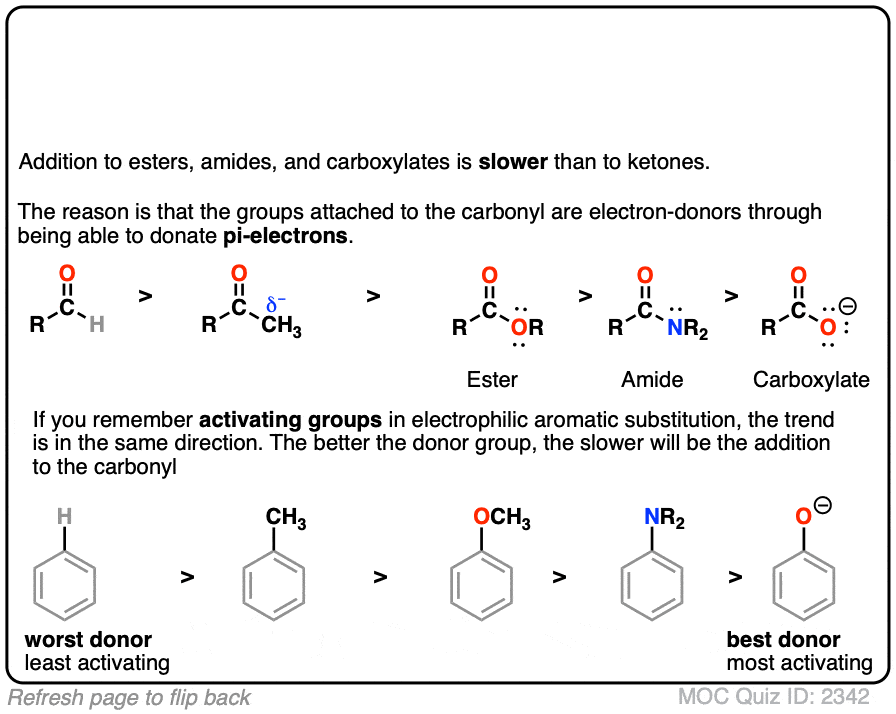
Quiz#: 2342
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
Which statements are correct / incorrect?
Quiz#: 986 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 987 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 988 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 989 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 990 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 991 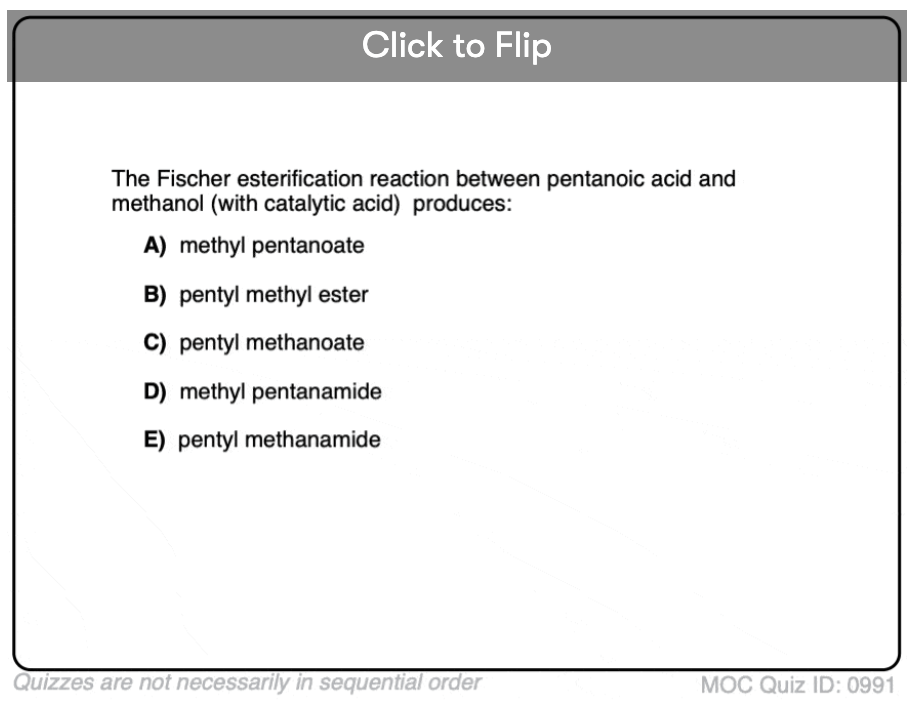
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 992 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 993 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 994 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 995 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 996 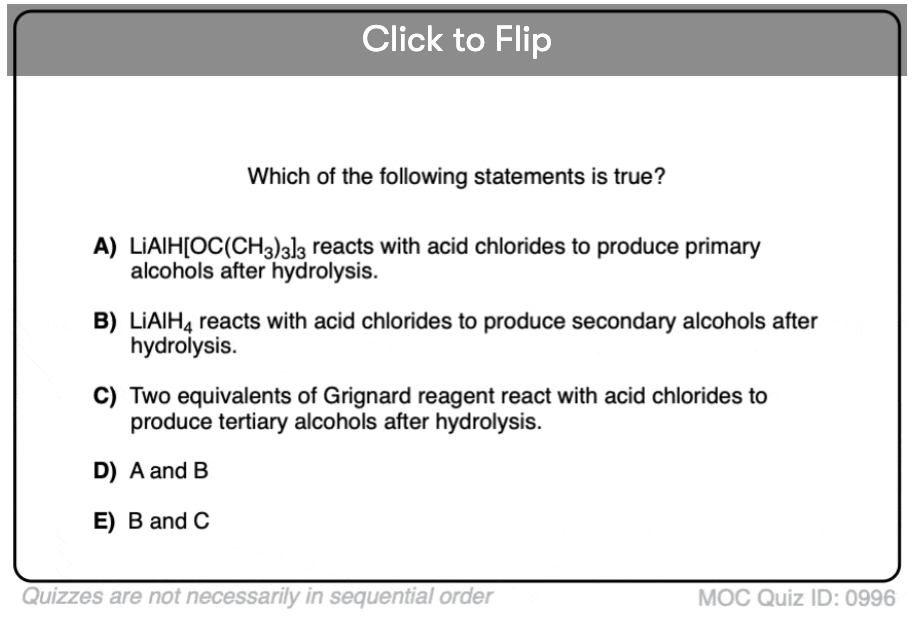
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 997 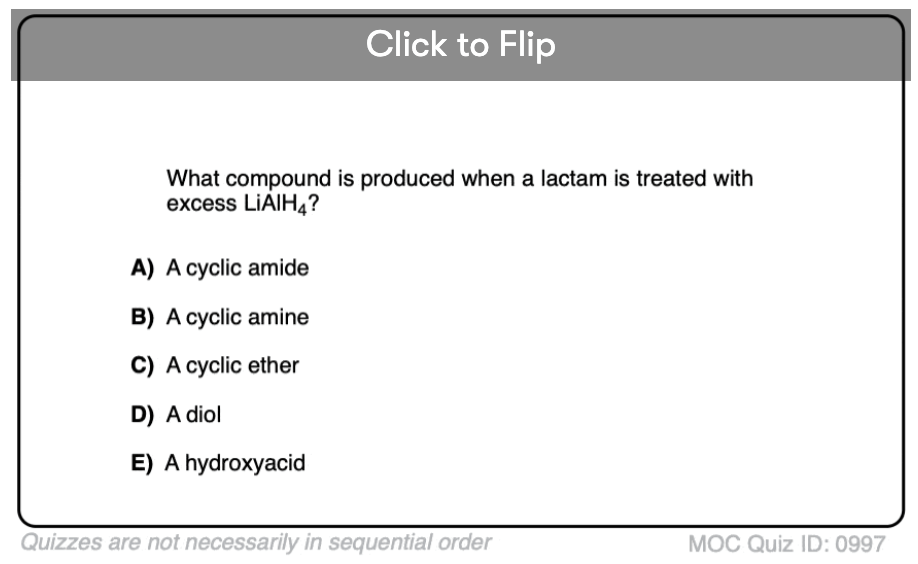
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 998 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 999 
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1000 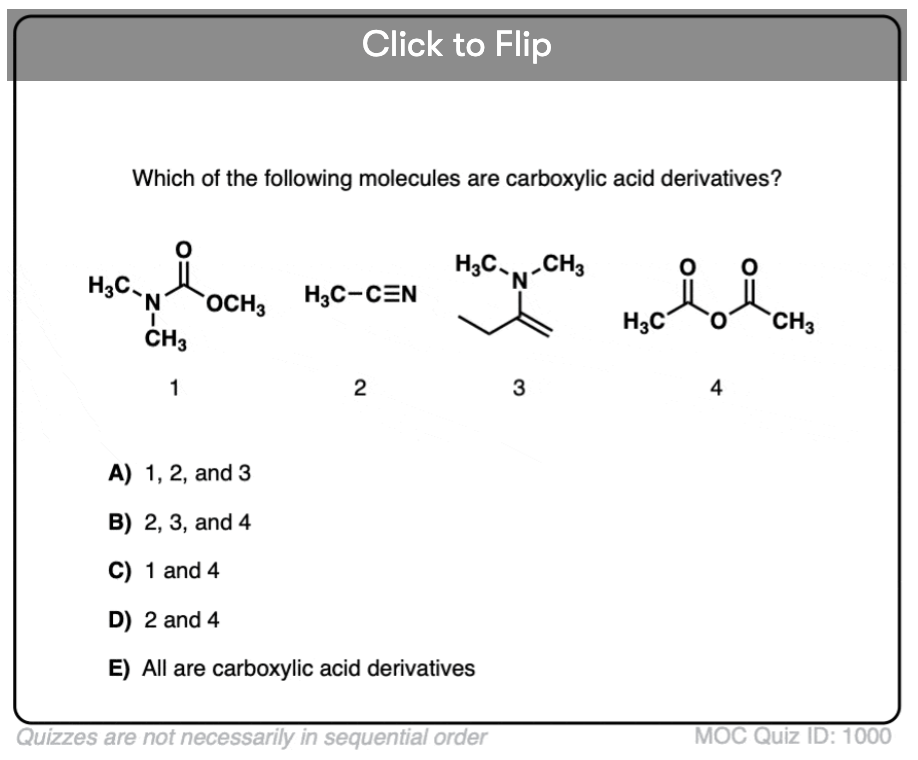
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
What is the major product?
Quiz#: 977 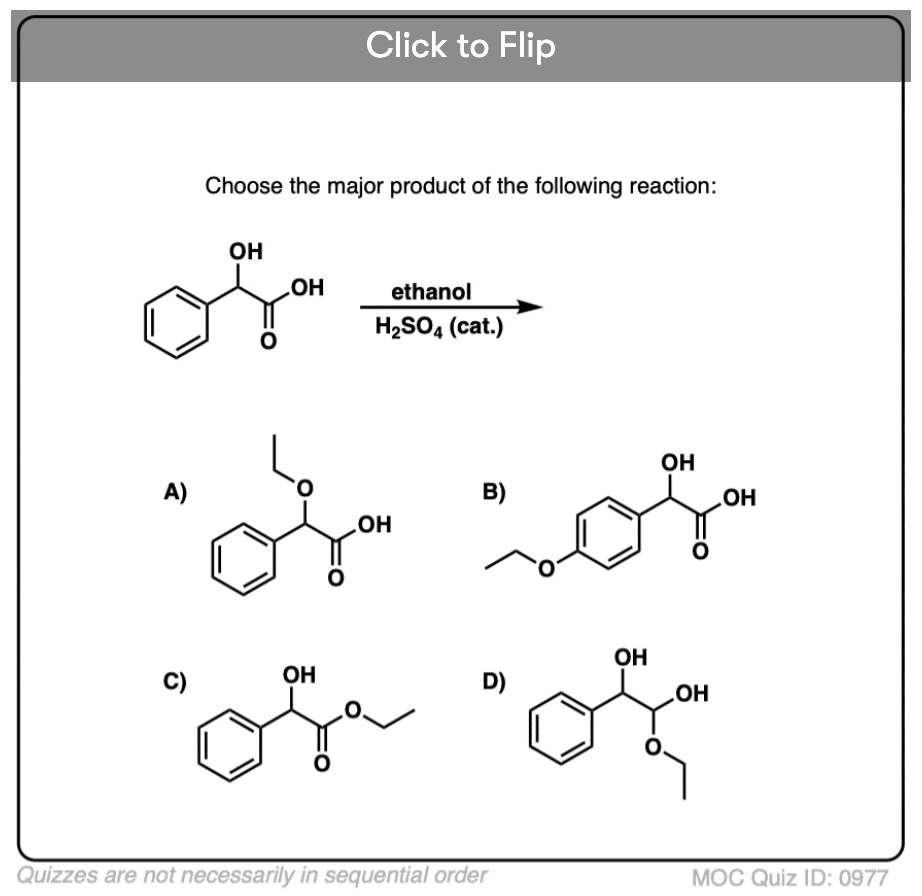
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 978 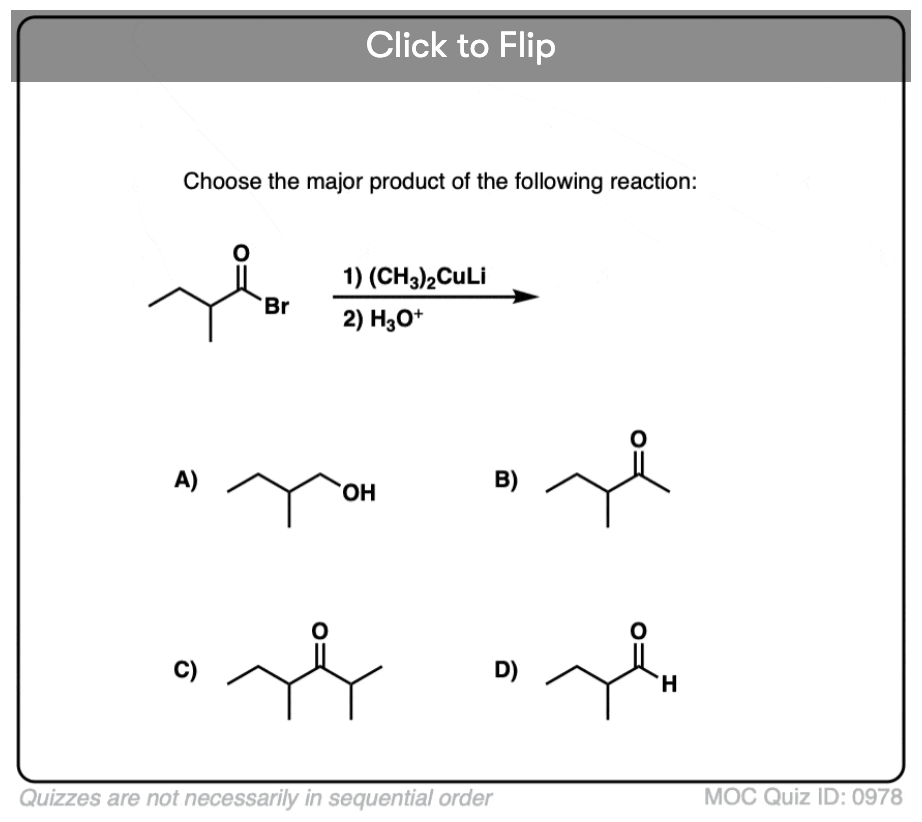
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 980 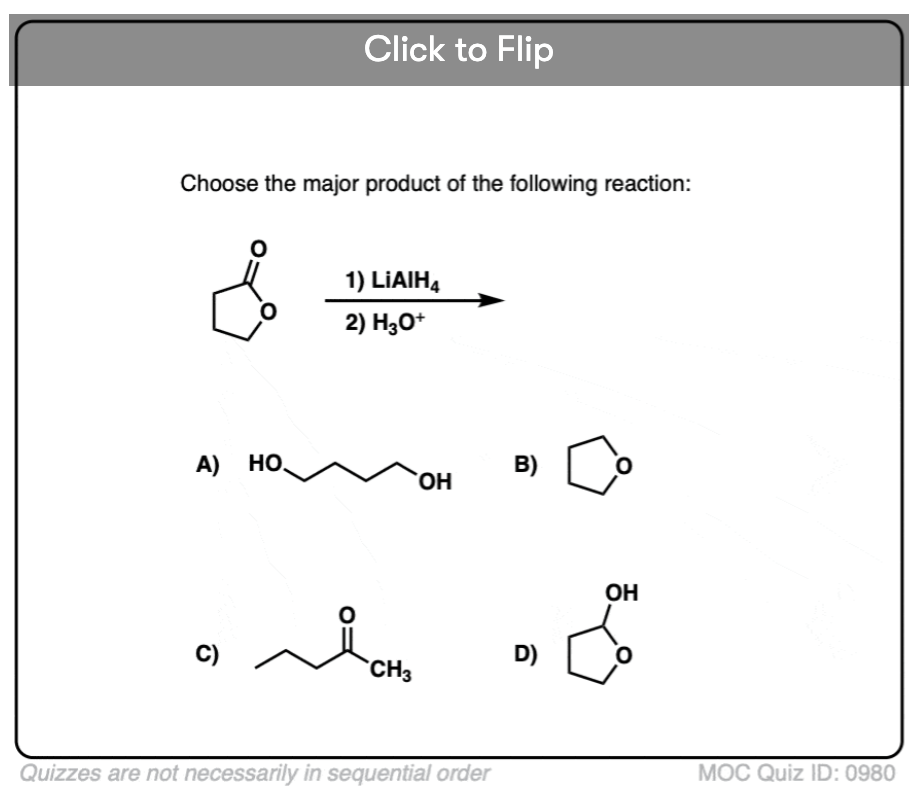
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 982 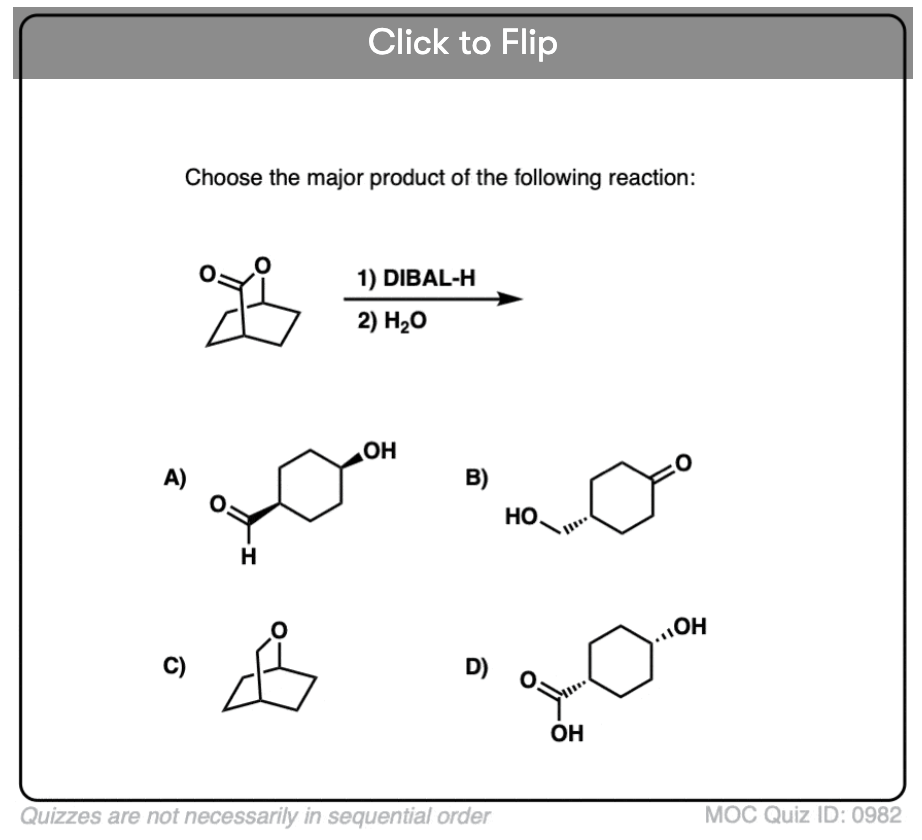
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 983 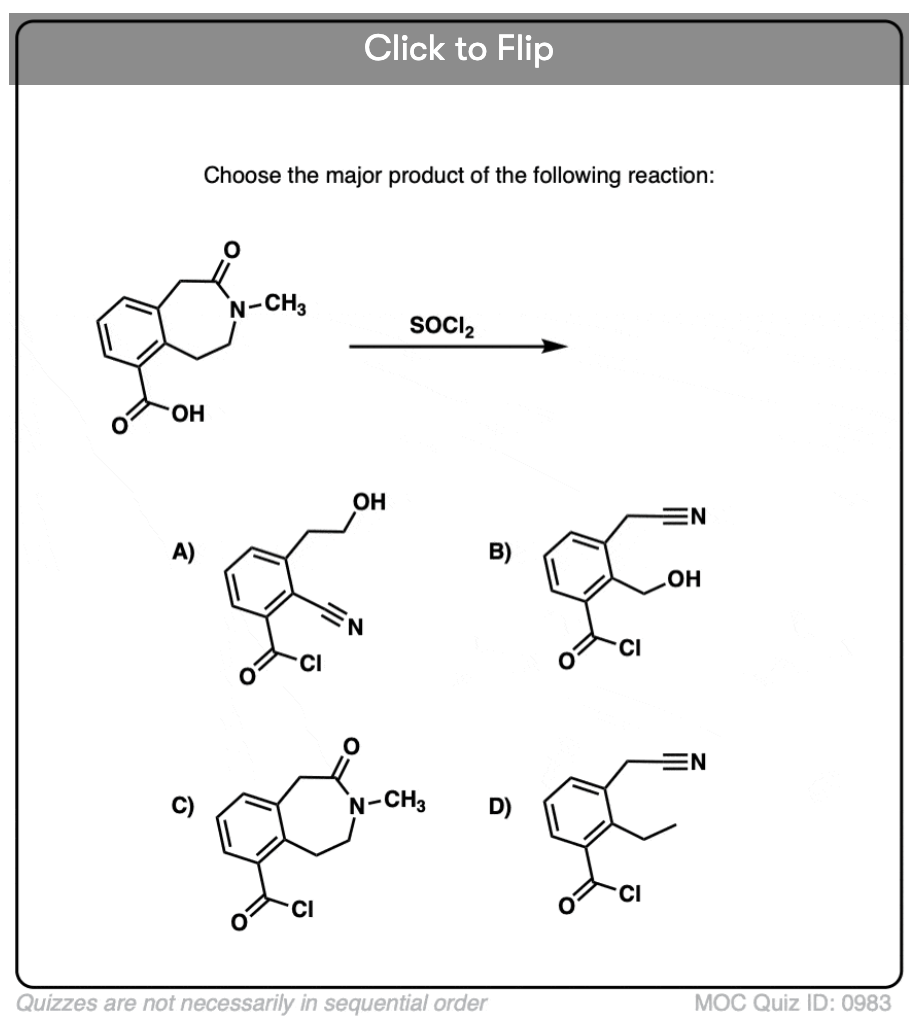
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 985 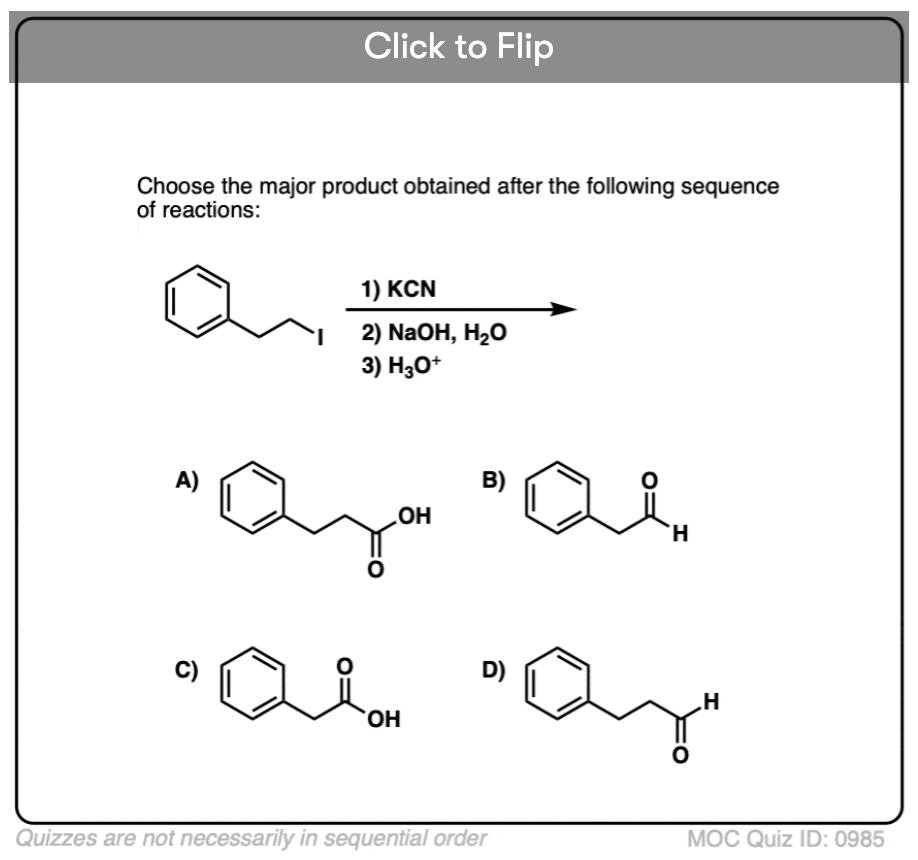
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 941 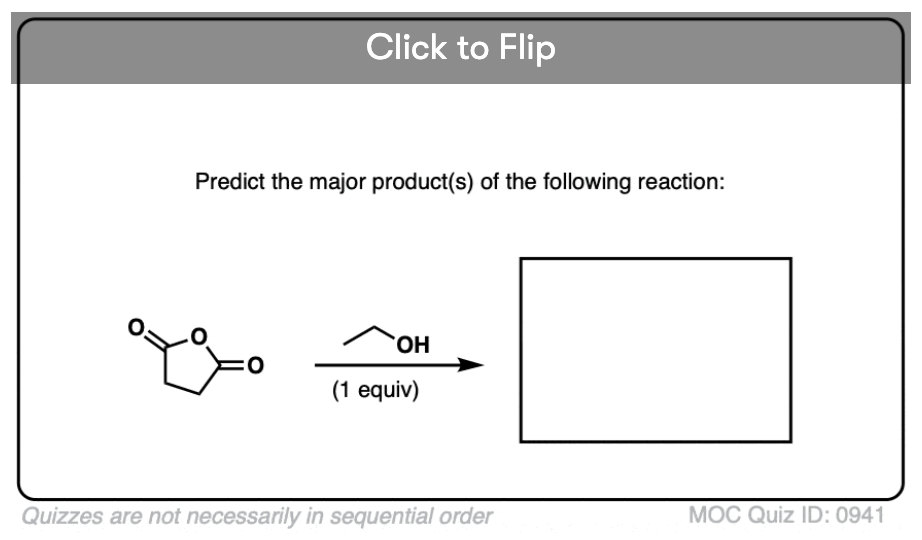
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 2453 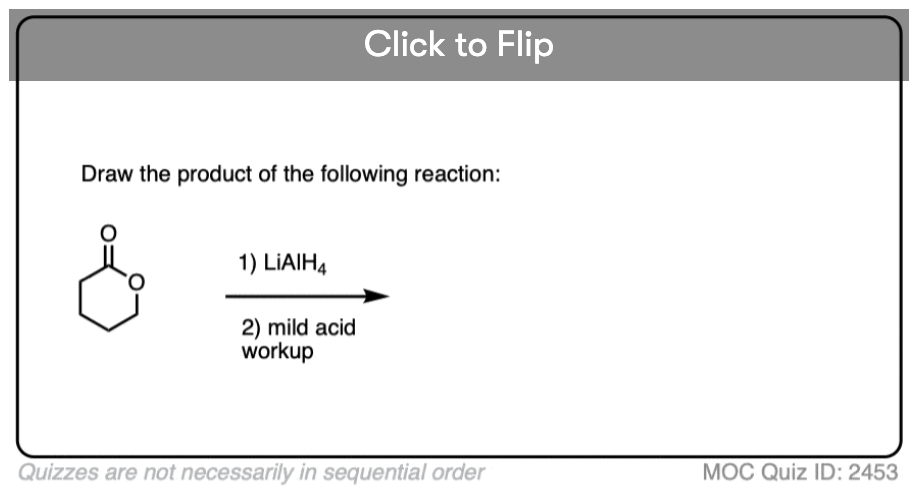
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 942 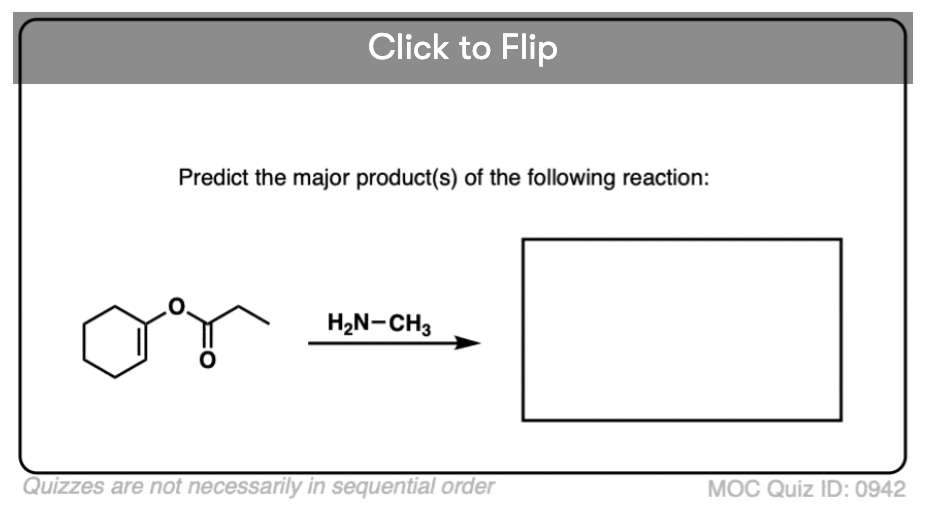
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 946 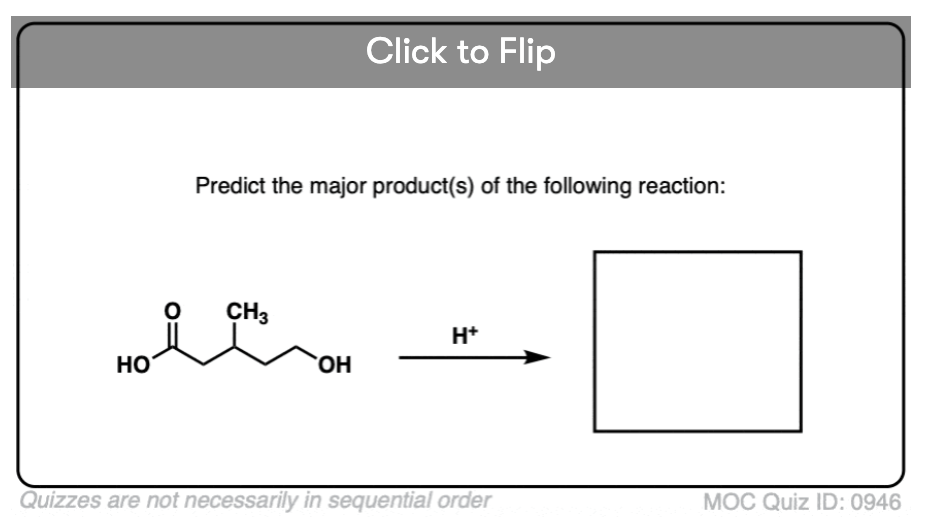
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 947 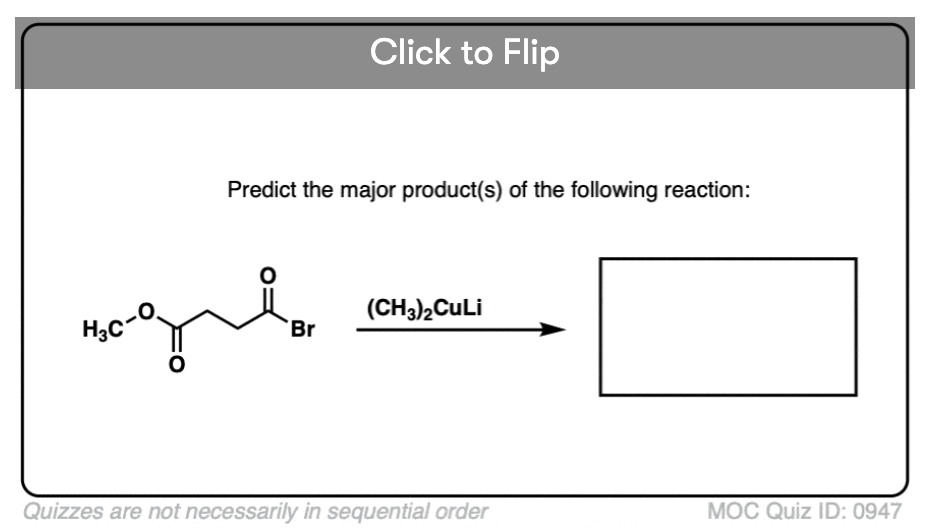
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 2072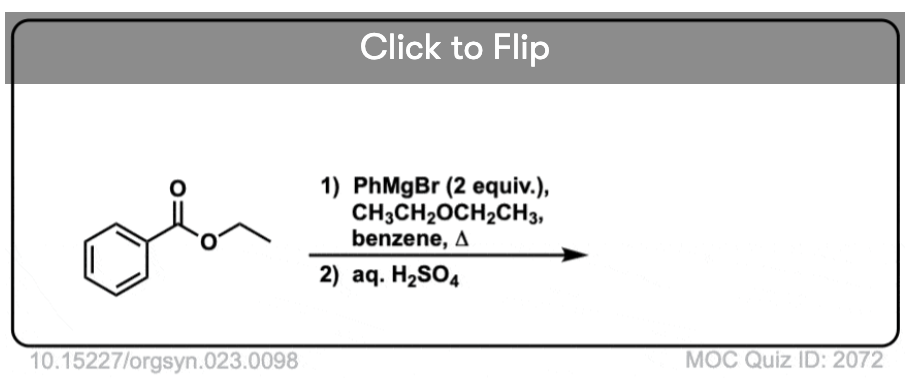
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 948 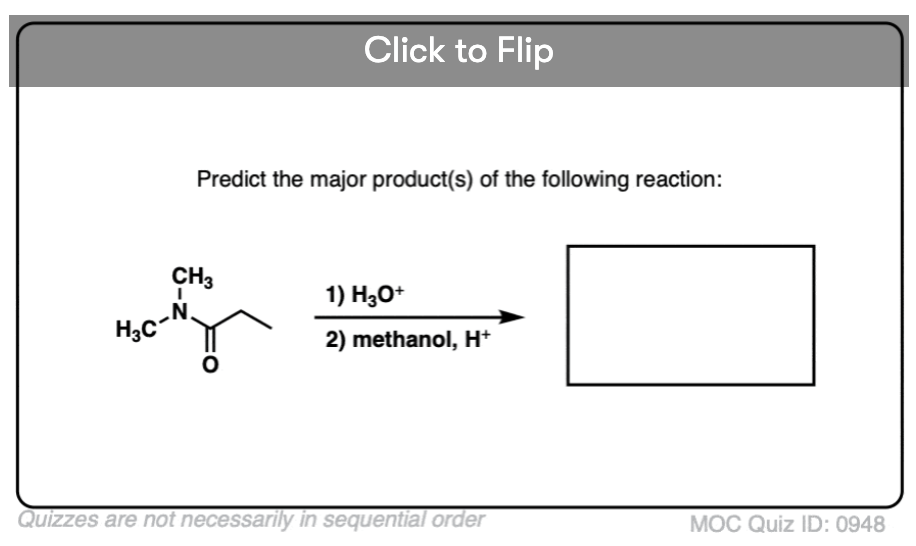
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 2452 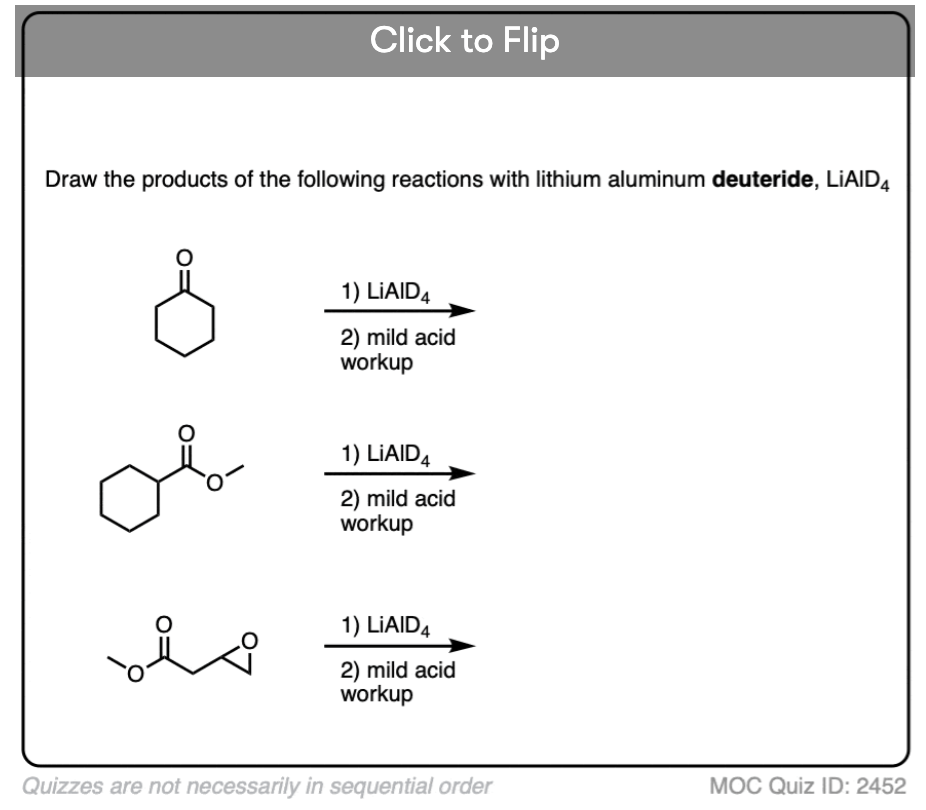
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
***Get access to about 45 more Carboxylic Acid quiz questions below by joining the MOC Membership ***
The rest of this page is available to MOC Members only.
To get access to this page, plus over 2500 quizzes, the Reaction Encyclopedia, Org 1 / Org 2 summary sheets, and flashcards, sign up here for only 30 cents/ day!