Epoxide Reaction Quizzes
Table of Contents
These practice questions cover the properties, formation, and reactions of epoxides, including their mechanisms.
Quiz count: 40
Properties of epoxides
Quiz#: 1415
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip

Formation of epoxides
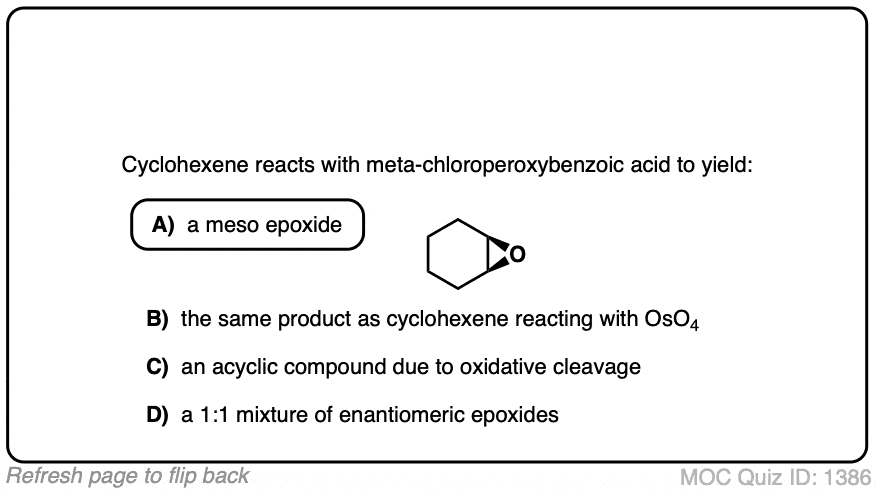
Quiz#: 1386
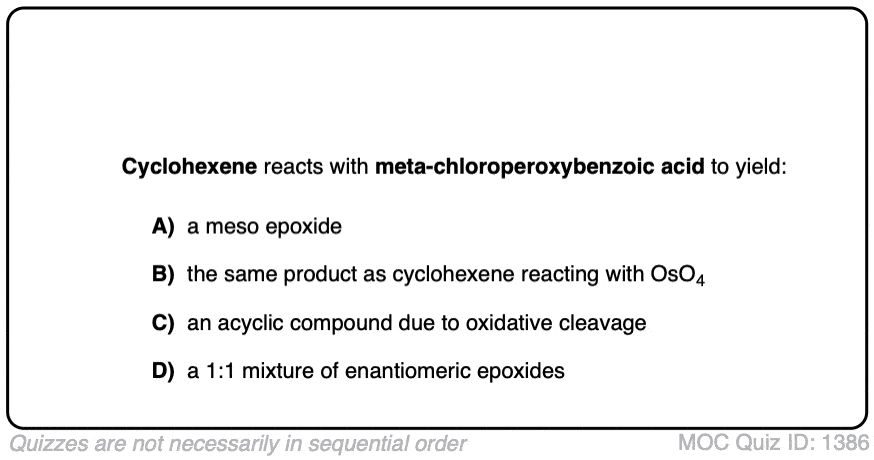 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
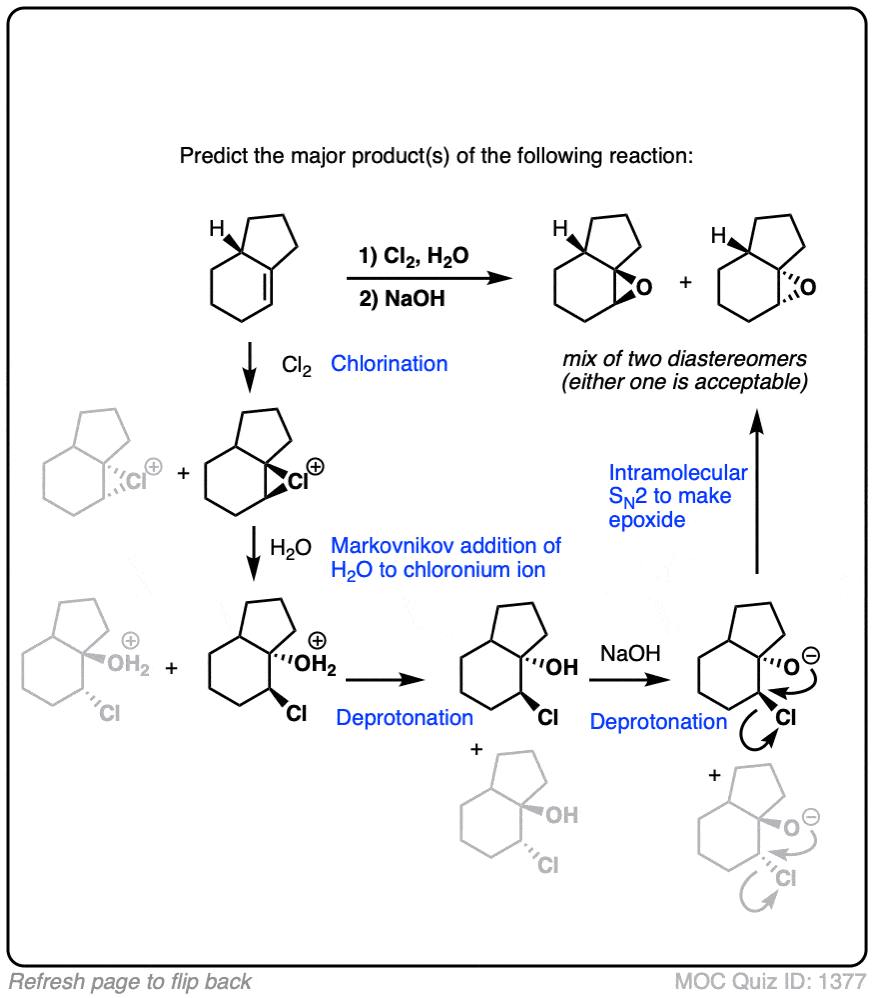
Quiz#: 1377
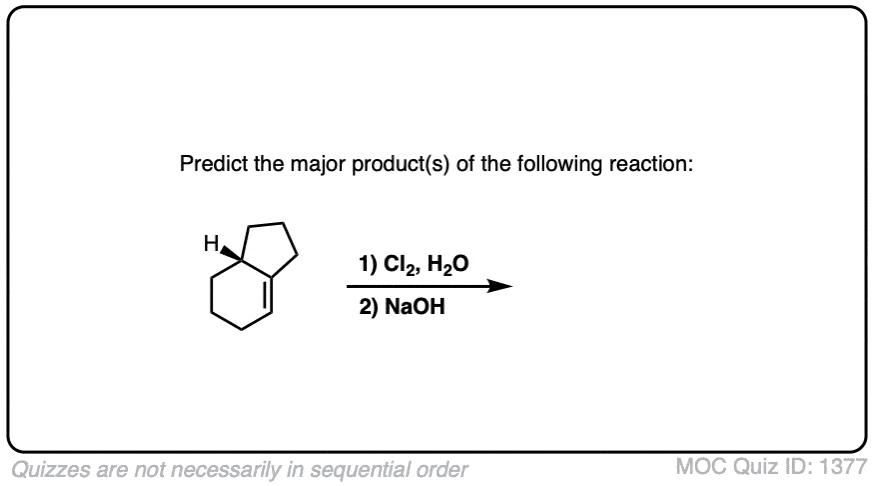 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
Quiz#: 1379
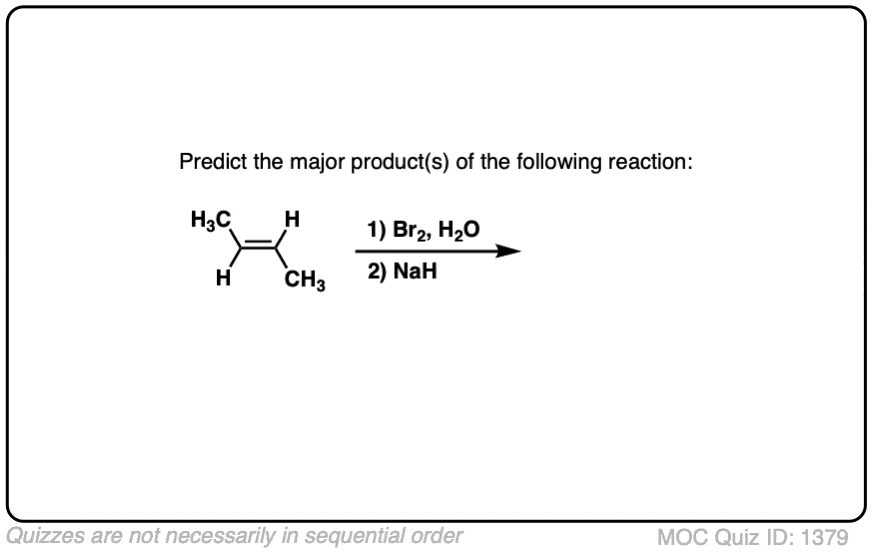 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
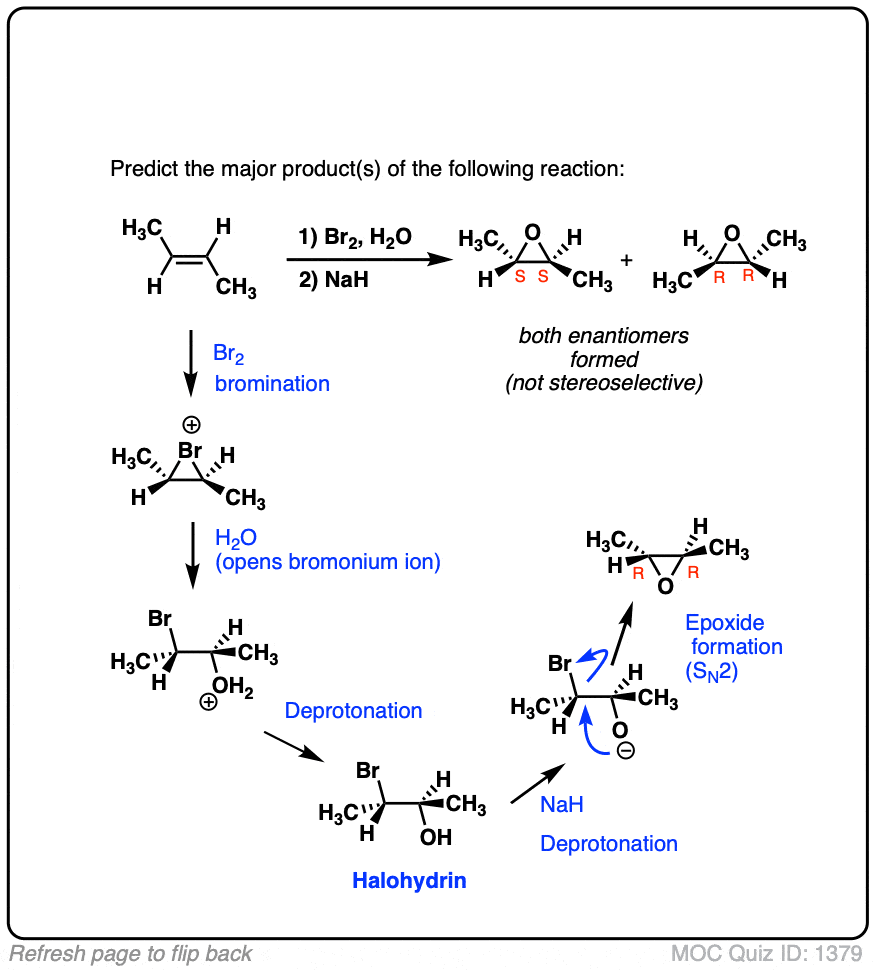
Quiz#: 1380
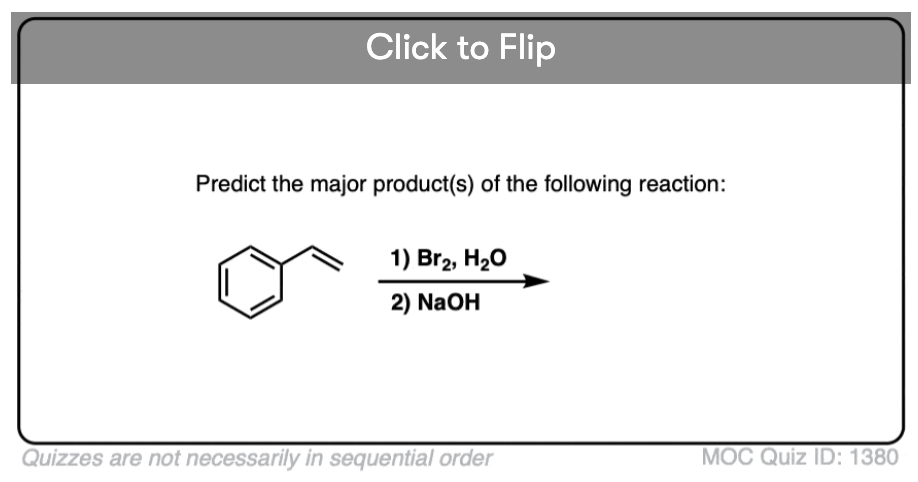
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1381
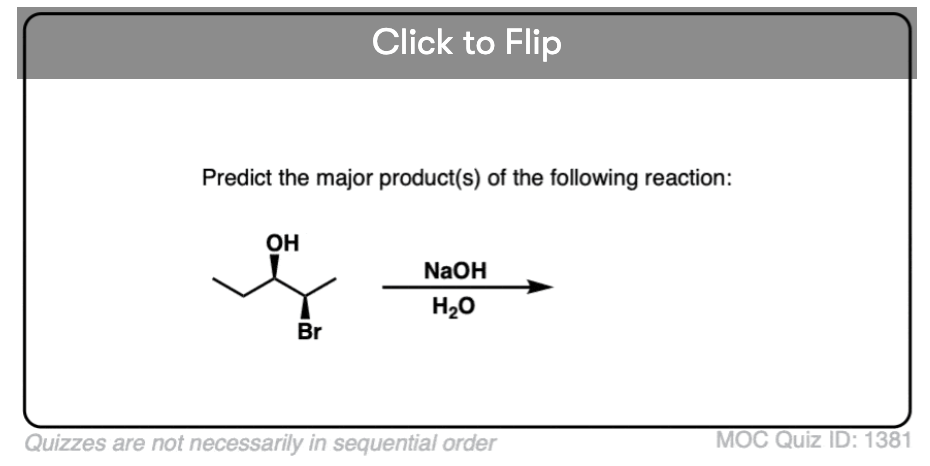
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1382
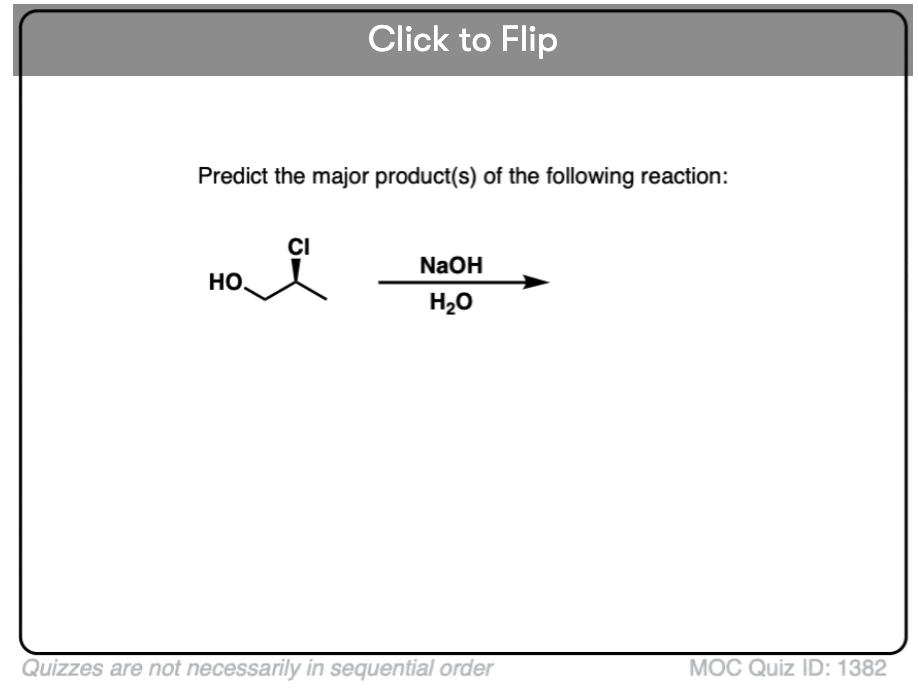
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1384
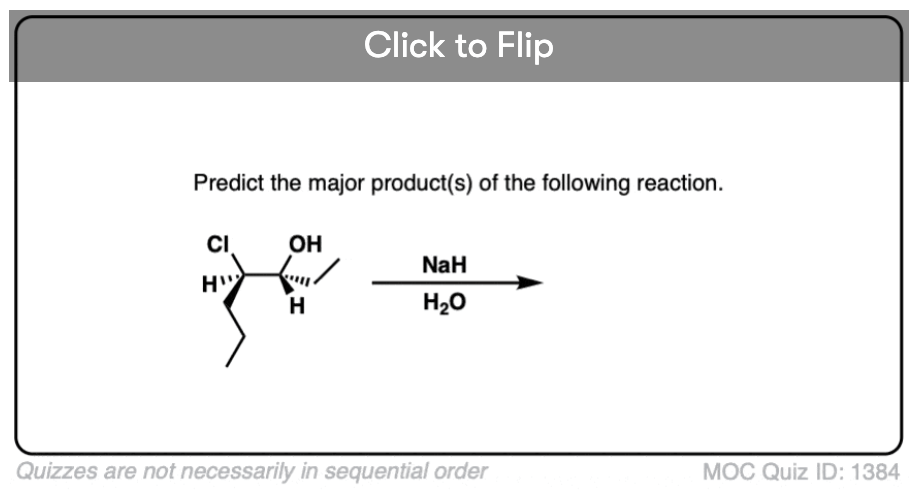
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Back to Top
Quiz#: 1385
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1387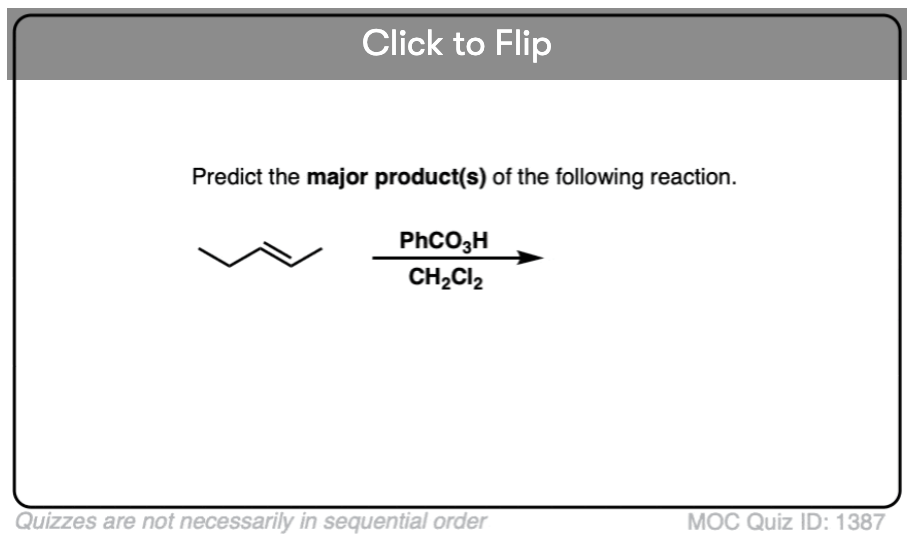
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1388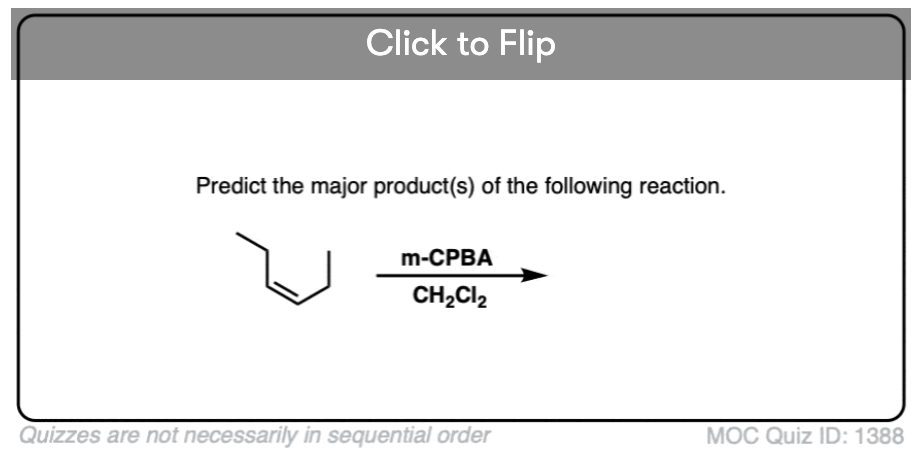
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1389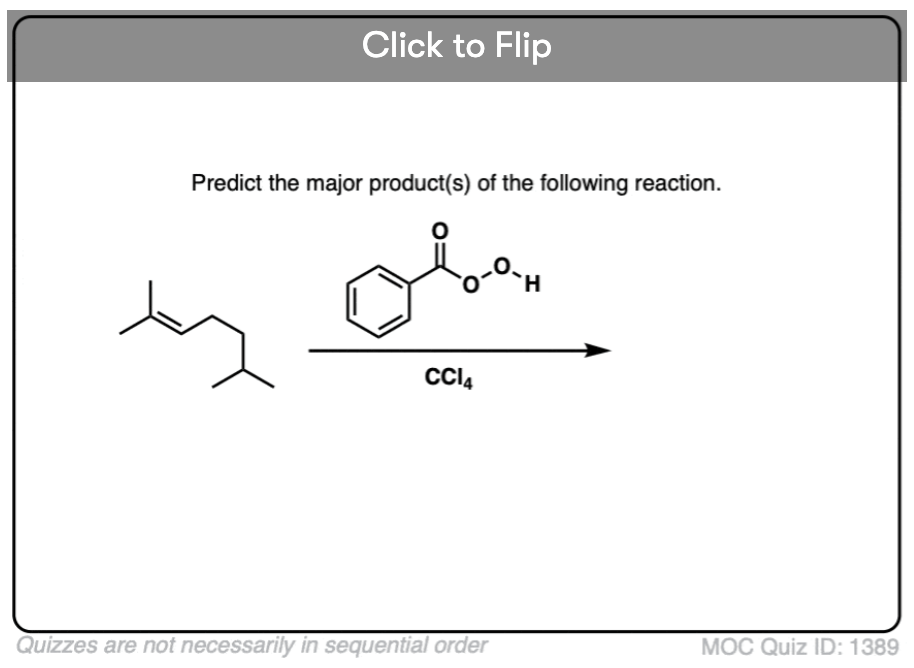
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1390
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1383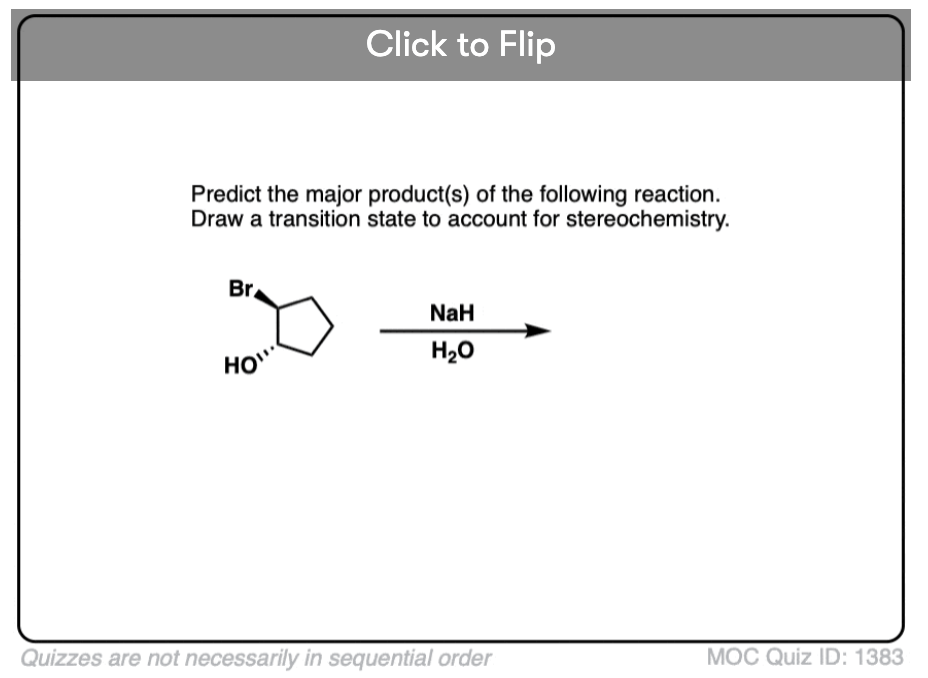
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1378 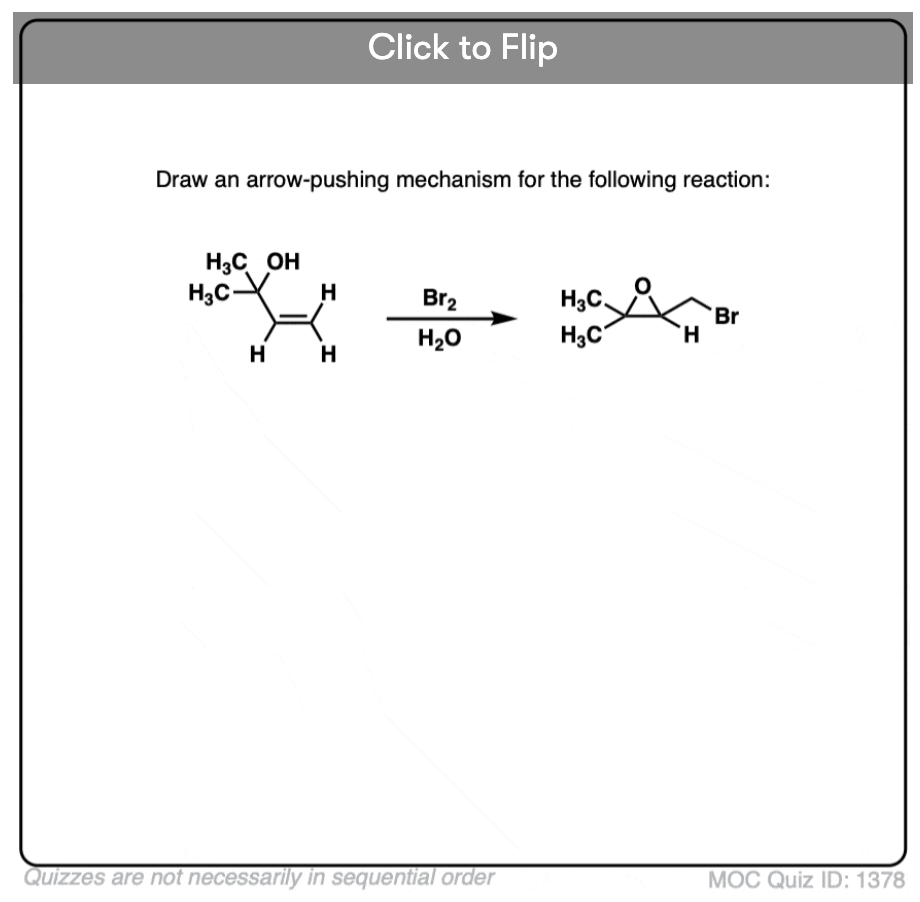
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Reactions of epoxides with nucleophiles
Quiz#: 1393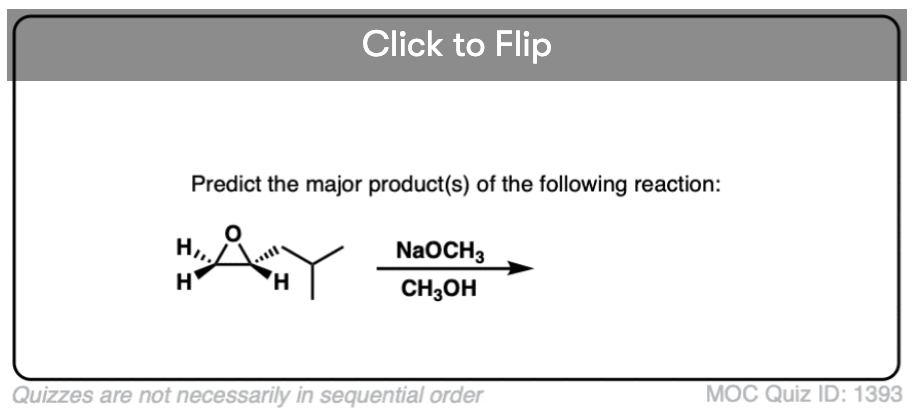
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1394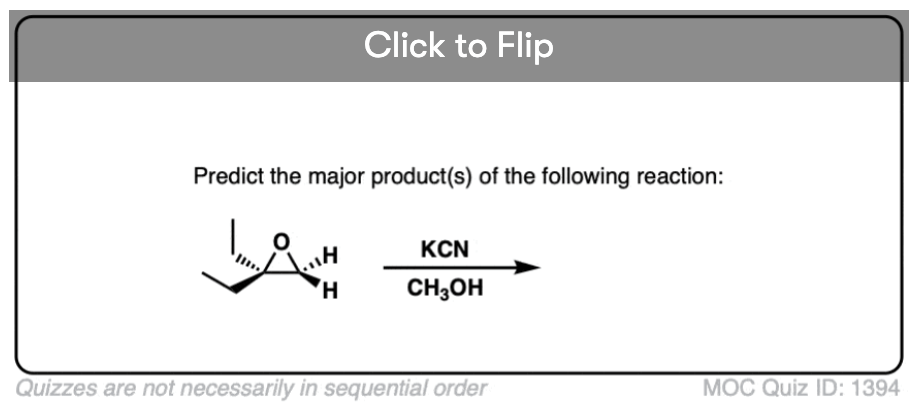
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 693
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
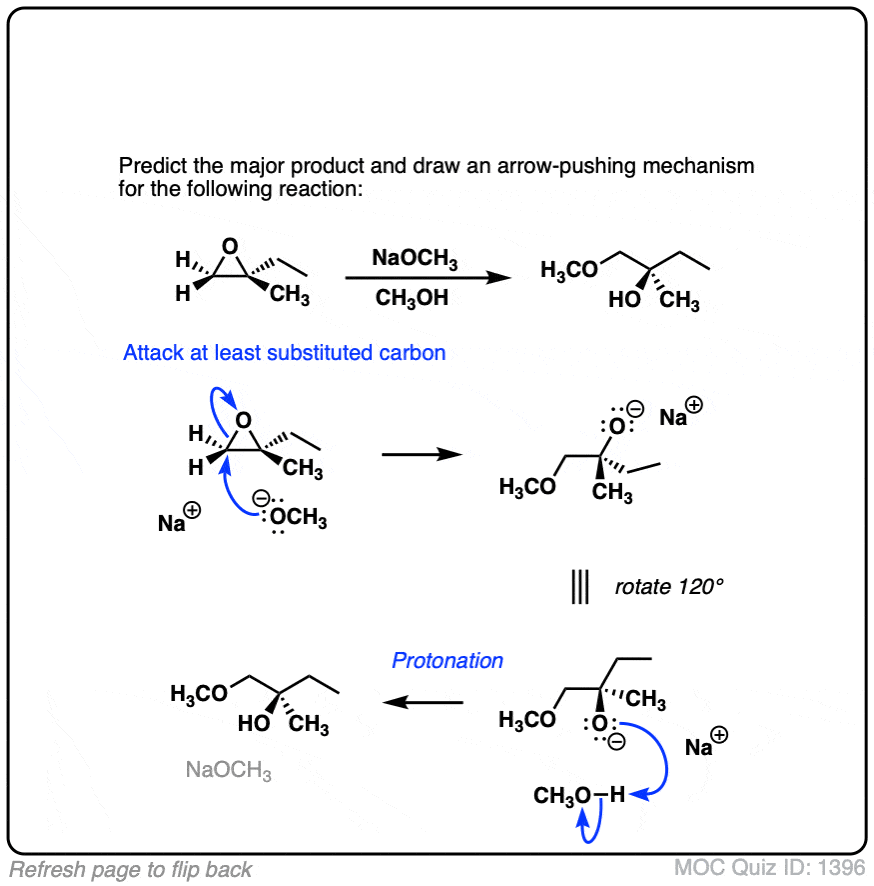
Quiz#: 1395
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1397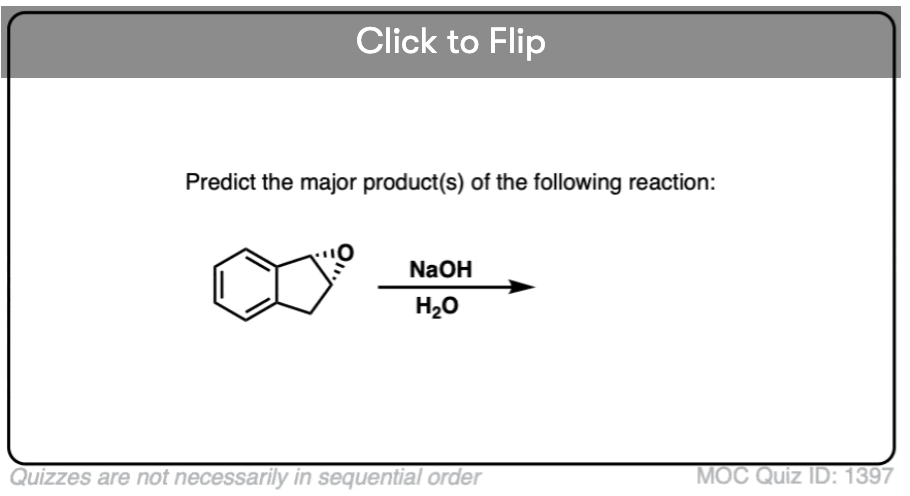
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1398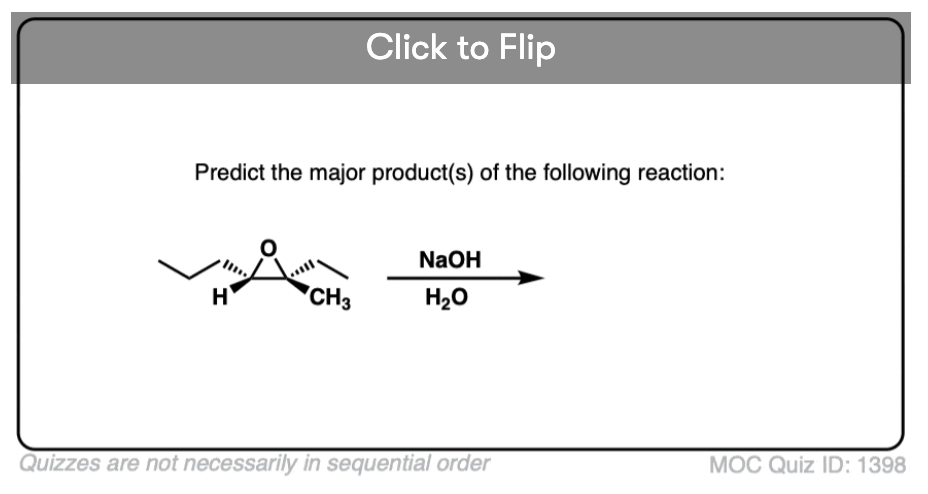
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1400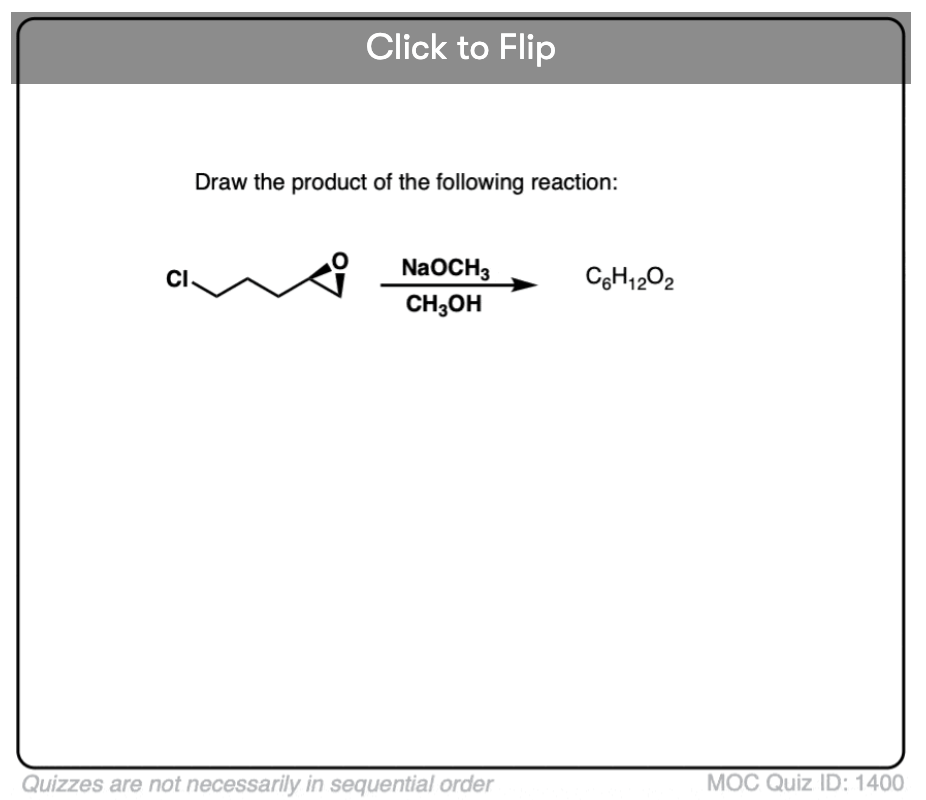
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Back to Top
Quiz#: 1410
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1411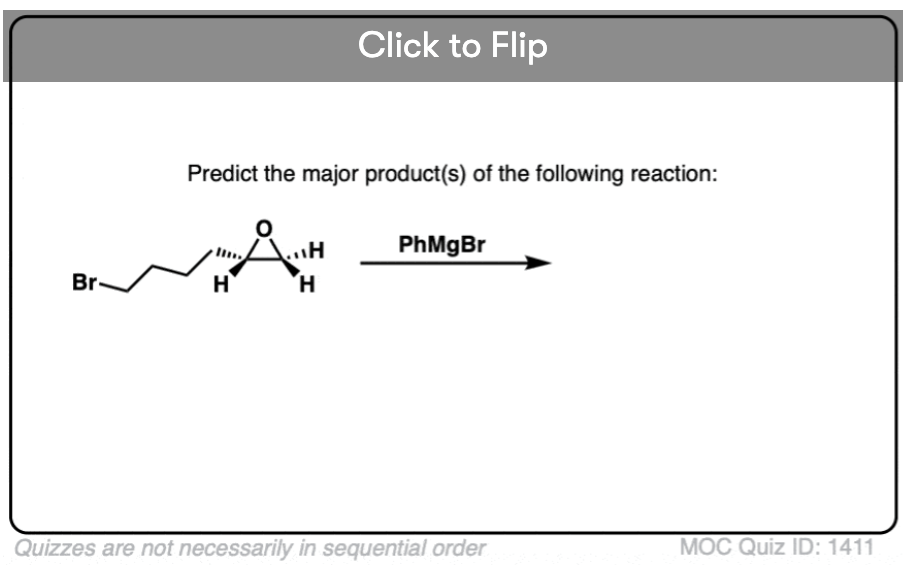
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1412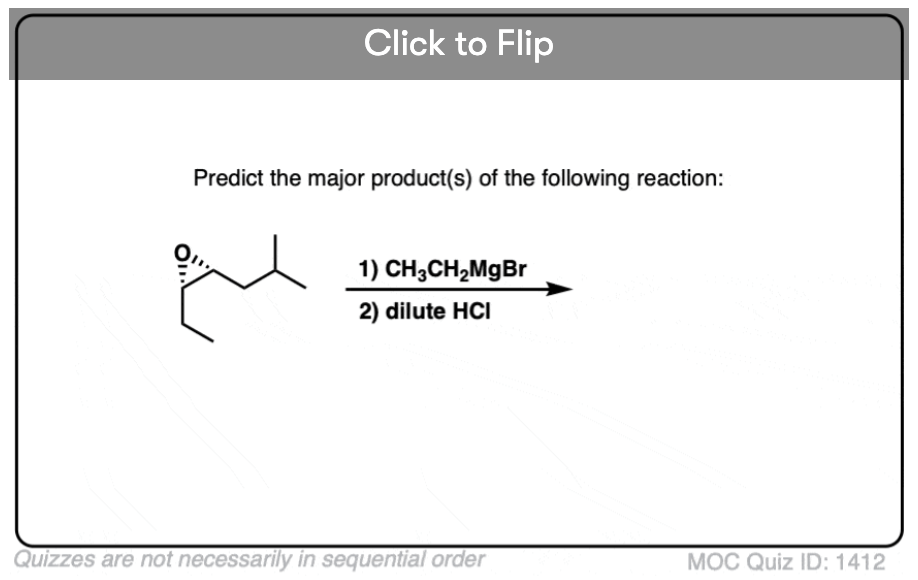
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1413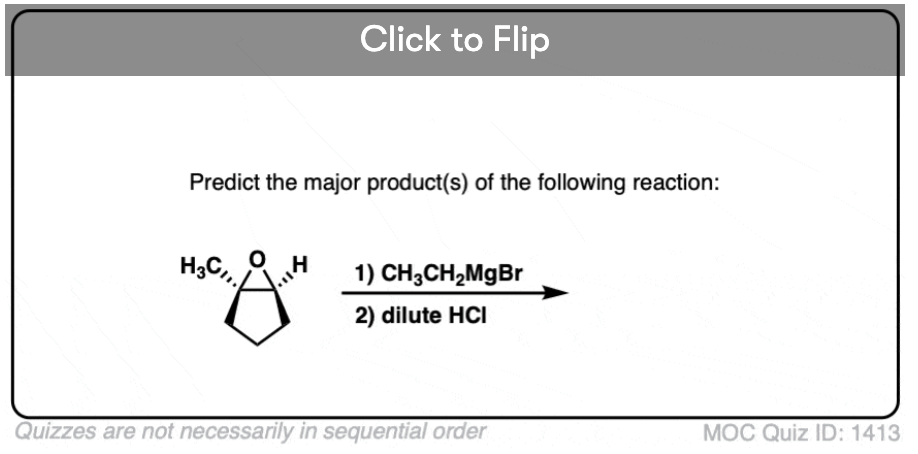
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1416
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1417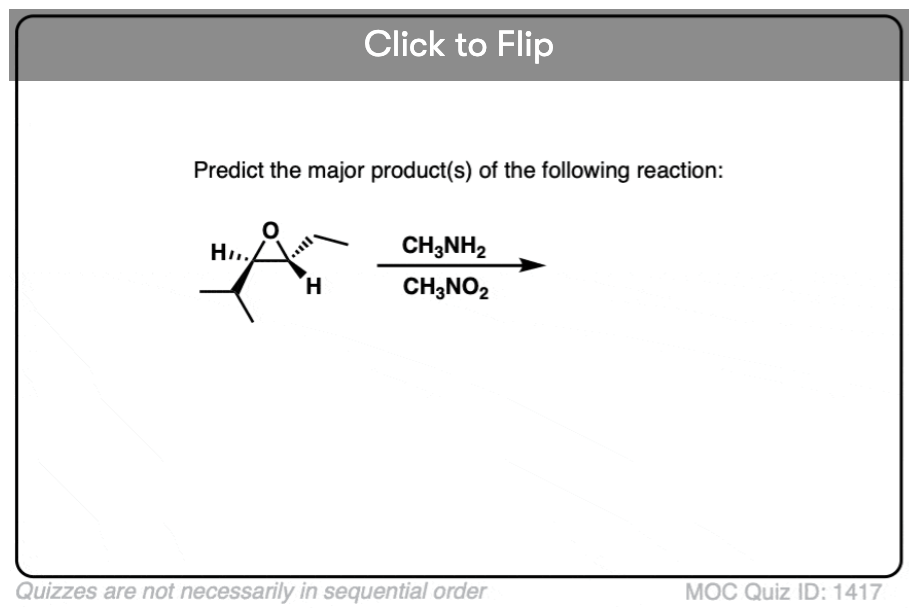
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.Quiz#: 1395
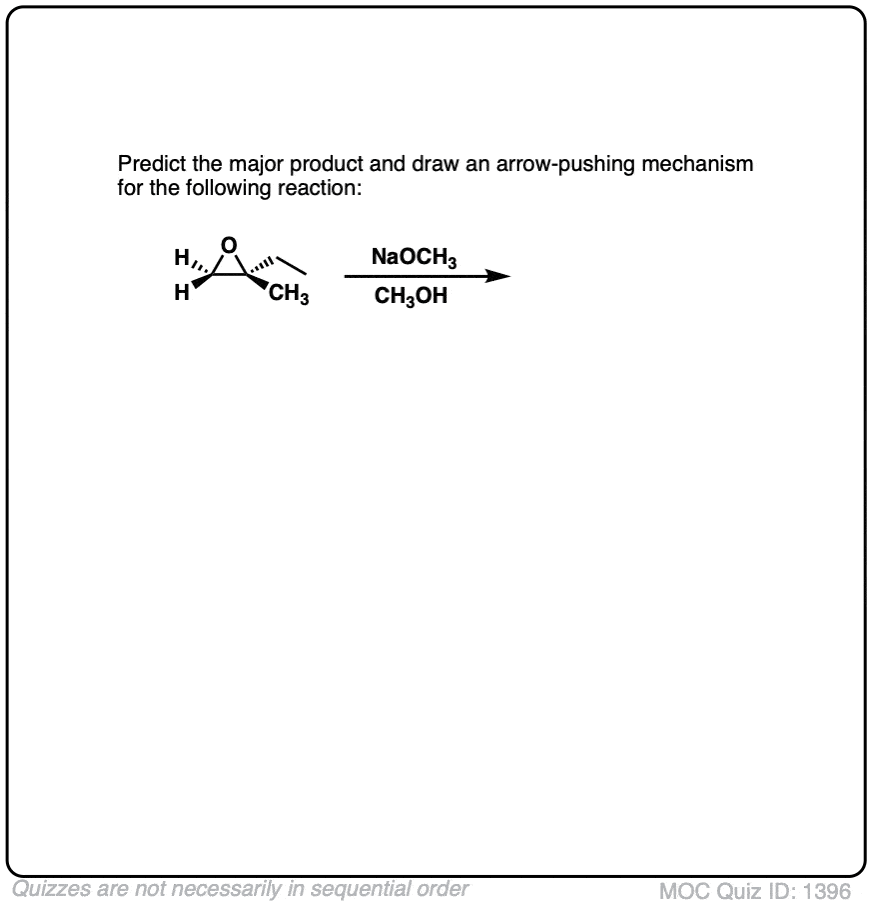 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
Quiz#: 1414
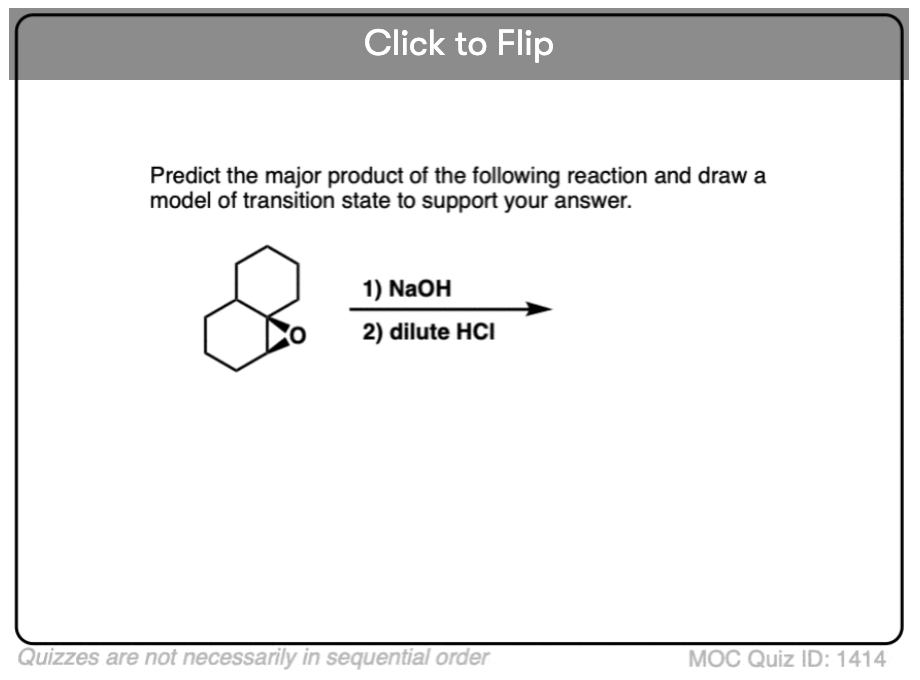
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1455
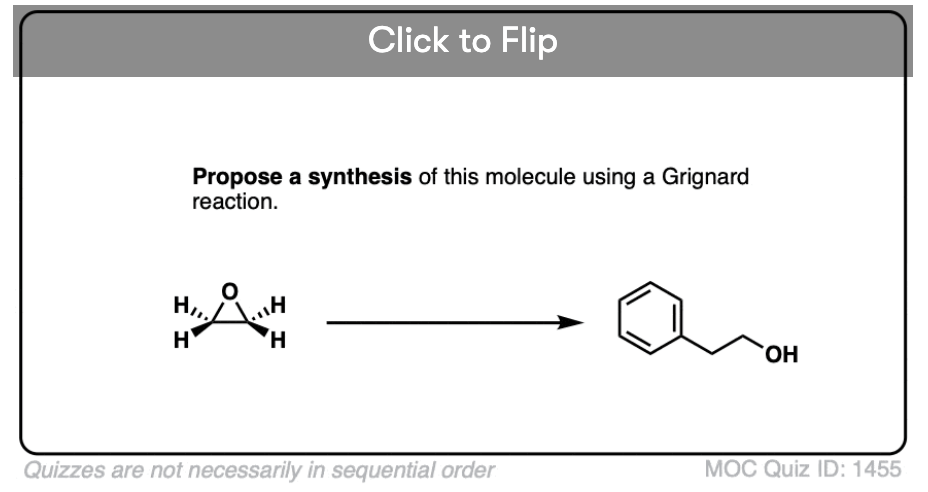
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Reactions of epoxides under acidic conditions
Quiz#: 1401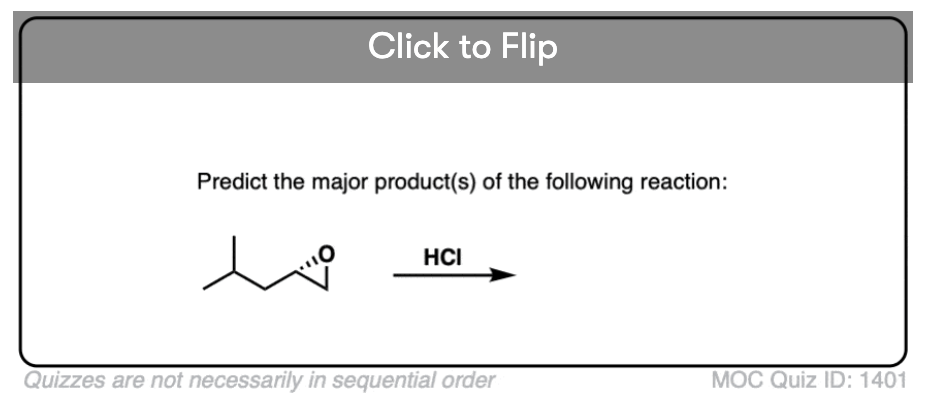
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
Quiz#: 1402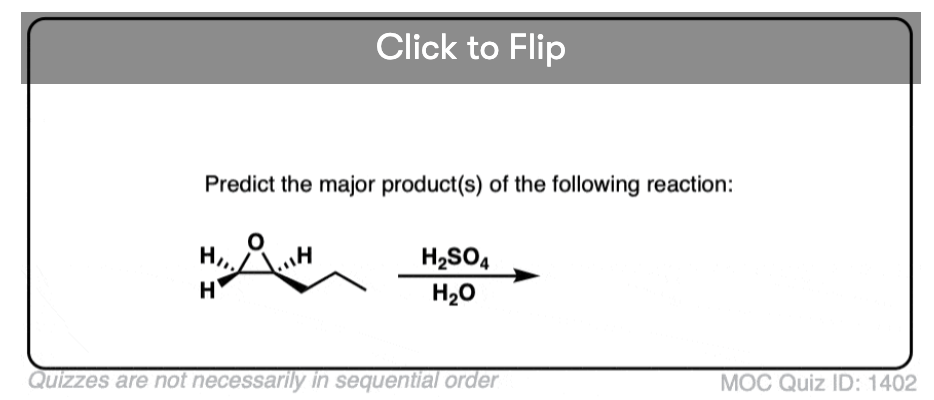
Become a MOC member to see the clickable quiz with answers on the back.
***Get access to about 10 more quiz questions below by joining the MOC Membership ***
The rest of this page is available to MOC Members only.
To get access to this page, plus over 2500 quizzes, the Reaction Encyclopedia, Org 1 / Org 2 summary sheets, and flashcards, sign up here for only 30 cents/ day!