SN2 of Cyanide with Alkyl Halides to give Nitriles
Description: Alkyl halides (or tosylates) will react with cyanide ion to give alkyl cyanides (nitriles) in an SN2 reaction.
The rest of this page is available to MOC Members only.
To get access to this page, plus over 2500 quizzes, the Reaction Encyclopedia, Org 1 / Org 2 summary sheets, and flashcards, sign up here for only 30 cents/ day!
Real-Life Examples:
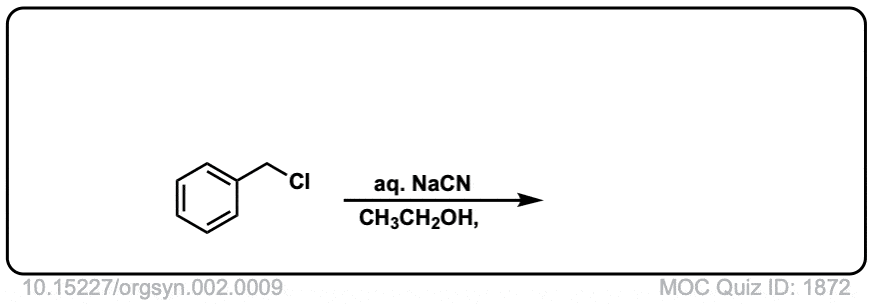
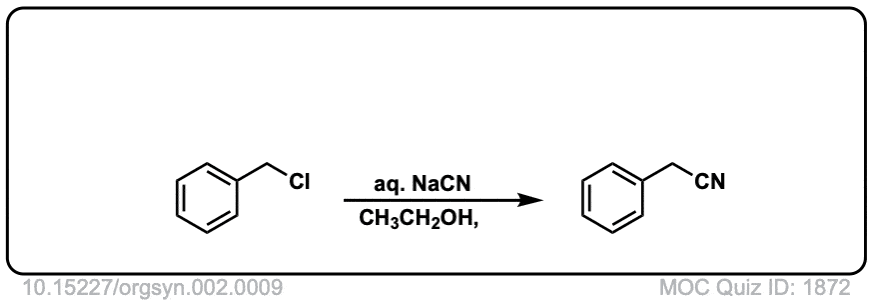
Org. Synth. 1922, 2, 9
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.002.0009
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
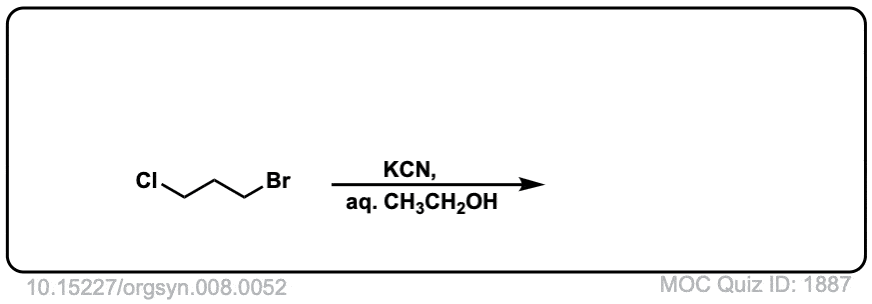
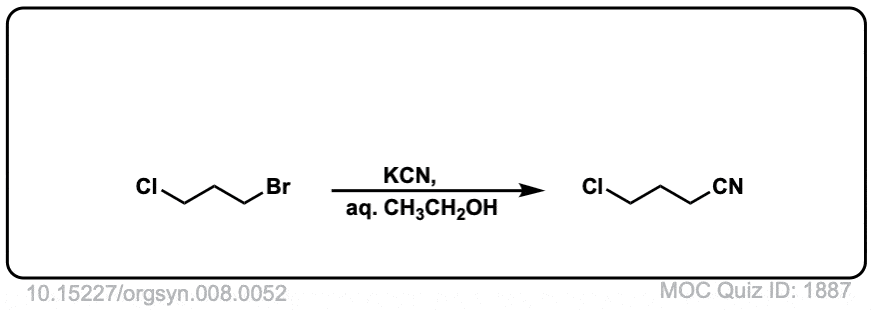
Org. Synth. 1928, 8, 52
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.008.0052
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
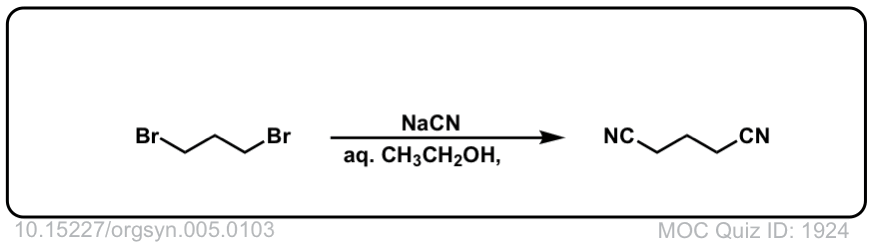
Org. Synth. 1925, 5, 103
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.005.0103
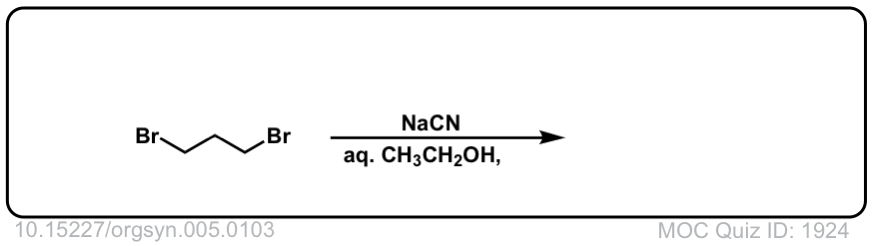 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
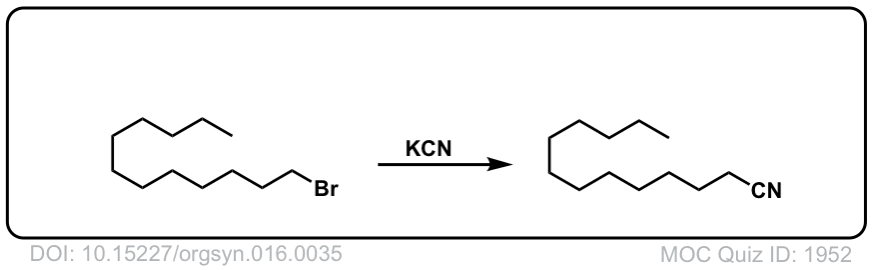
Org. Synth. 1936, 16, 35
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.016.0035
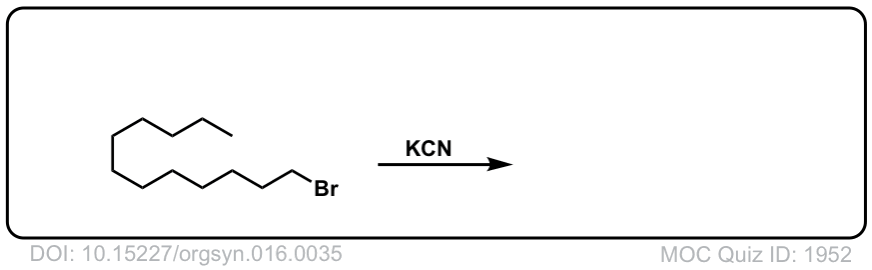 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
Org. Synth. 1938, 18, 50
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.018.0050
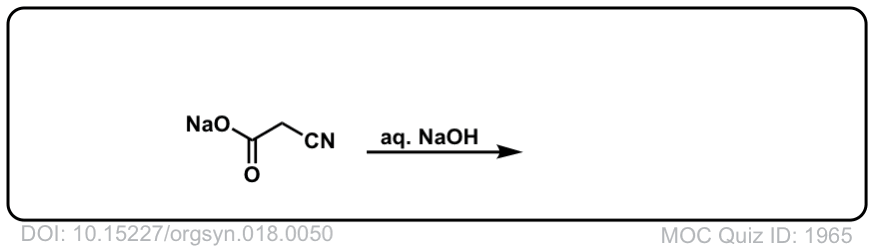 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
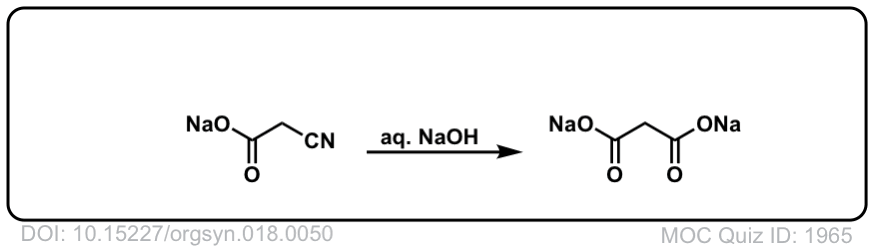
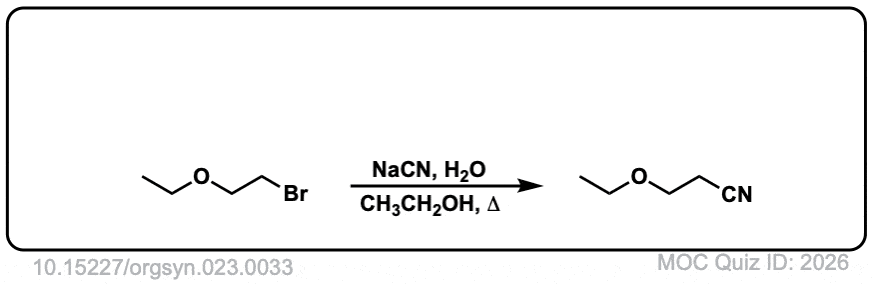
Org. Synth. 1943, 23, 33
DOI link: 10.15227/orgsyn.023.0033
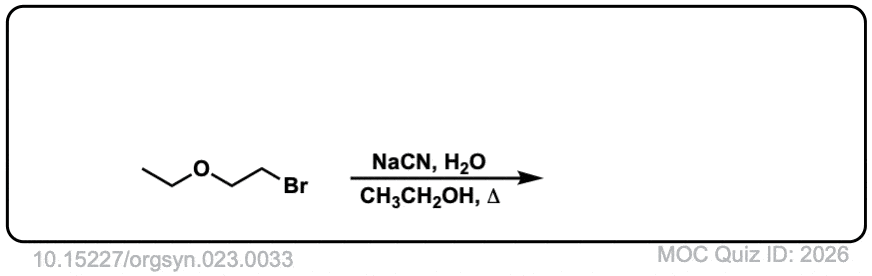 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
What if you add CH2CN to the reaction as well? Instead of just CN?
Do you mean CH3CN ? Acetonitrile? That’s a polar aprotic solvent, should be a great solvent for a reaction like this.
Hi,
The first example reaction is for acetal formation…not alkyl halides for nitriles. Other than that, this is fantastic! Finally understand reactions properly! :)
the work is good, i real like it.