Friedel Crafts alkylation of arenes
Description: In the presence of a catalyst such as FeCl3 or AlCl3 treatment of an aromatic with an alkyl chloride provides an aromatic alkane. This reaction is called “Friedel-Crafts alkylation” .
This page is available to MOC Members only.
Sign up here for about 30 cents/ day!
Real-Life Examples:
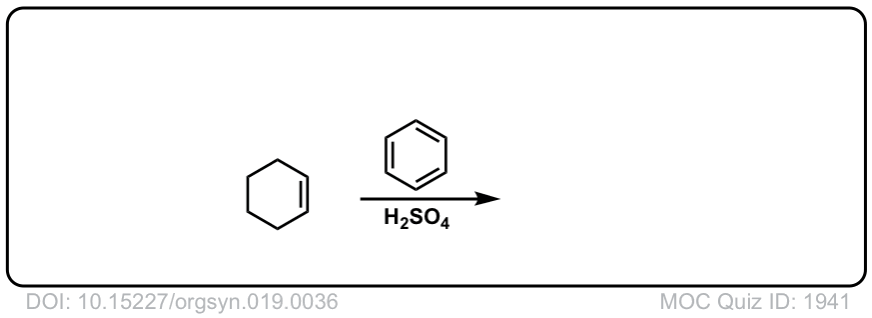
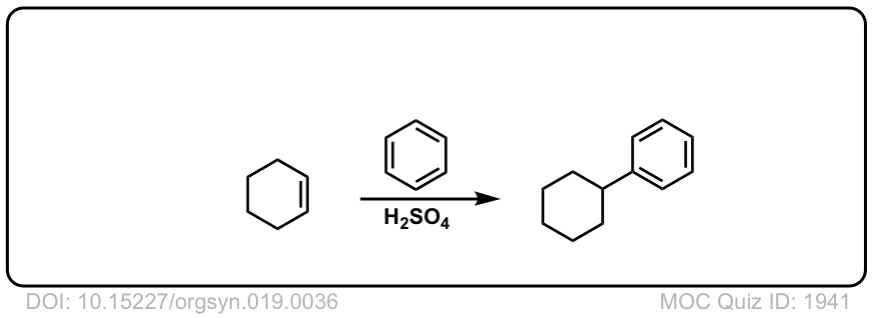
Org. Synth. 1939, 19, 36
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.019.0036
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
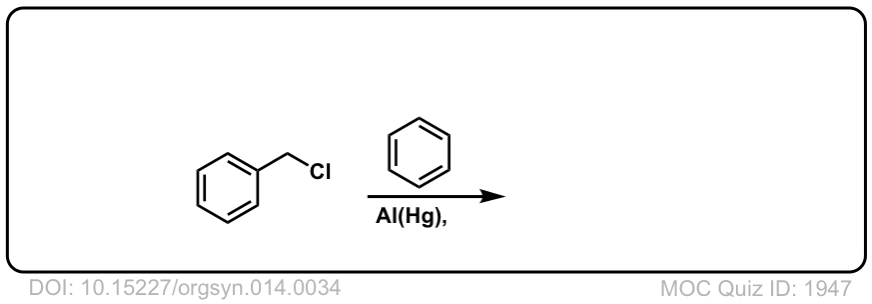
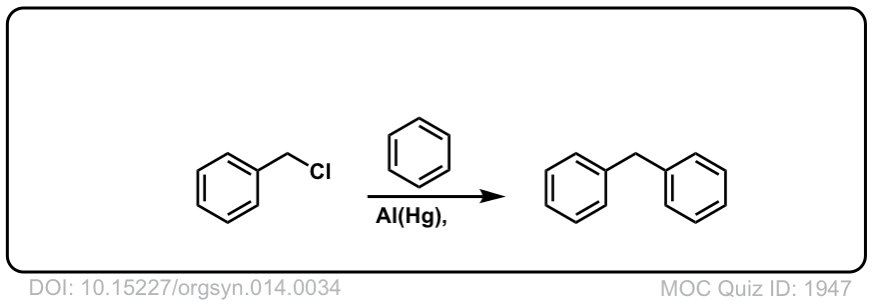
Org. Synth. 1934, 14, 34
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.014.0034
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
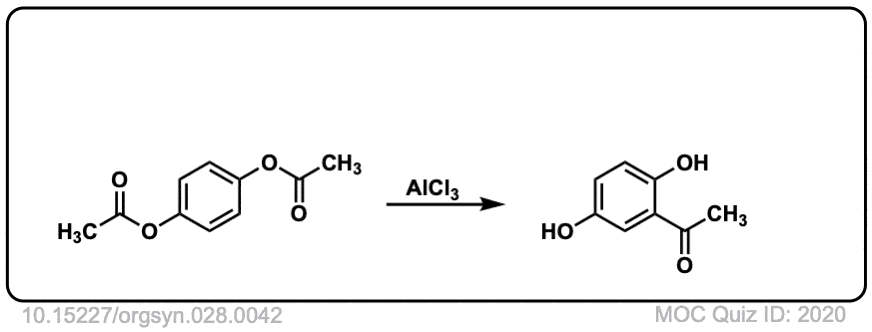
Org. Synth. 1948, 28, 42
DOI Link: 10.15227/orgsyn.028.0042
 Click to Flip
Click to Flip
In example 2, why is AlCl3 needed? Why Cl doesn’t leave by itself like SN1 reactions because here it will form tertiary carbocation? Thank you
In example 6, there looks like there was a hydride shift that occurred within the iso-butyl group. Is that possible? I thought carbocation rearrangements could only occur if the neighboring carbon to carbocation had a hydrogen that it could donate
Yes – alkyl shifts can happen as well!
The alkyl halide is primary and becomes a primary carbocation when AlCl3 removes Cl. This primary carbocation becomes a tertiary carbocation through the shift of an alkyl group (CH3).
The tertiary carbocation is then attacked by the aromatic ring giving the final product.
I have a question, but Ive heard FC alkylation reaction makes multi-substitution product. And is it right if there is Halogen already in Benzene, FC makes only one-substitution product??
Thanks.
Yes, that is correct. Friedel-Crafts alkylation results in a more electron-rich aromatic ring, which can then compete with the starting aromatic ring for the electrophile. It’s a Cookie Monster reaction. If there is an electron-withdrawing substituent (like Cl) this will be less likely to happen.
Mechanism is spelled Mecbanism. I’m an orthographist by night.
in example 2, I thought aryl halides didn’t react in Friedel crafts alkylation?
They generally don’t occur when meta-directing groups are present, but FC alkylations are possible when a single halogen atom is present.