Home / The 4 Major Classes of Reactions in Org 1
Organic Chemistry Tips and Tricks
The 4 Major Classes of Reactions in Org 1
Last updated: January 23rd, 2024 |
Quiz time. Look at these reactions. Ask yourself this question for each: what bonds are broken, and what bonds are formed.
Don’t worry if you don’t understand the reactions. That comes later. You don’t need to understand the reactions to be able to answer this question.
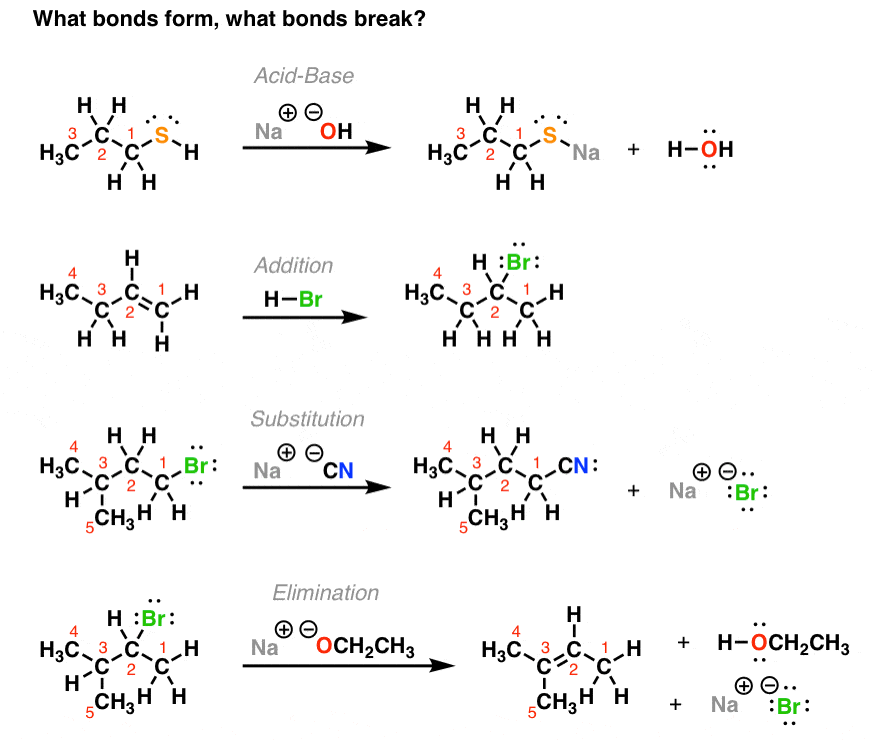
If you can do this successfully you are off to a good start. At least 80% of the reactions you will learn in Org 1 fall into one of these 4 categories. The sooner you can get into the habit of recognizing bond formation and breakage the better off you will be.
More about each of these patterns later.
Next Post In The Series: Introduction To Acid Base Reactions
00 General Chemistry Review
01 Bonding, Structure, and Resonance
- How Do We Know Methane (CH4) Is Tetrahedral?
- Hybrid Orbitals and Hybridization
- How To Determine Hybridization: A Shortcut
- Orbital Hybridization And Bond Strengths
- Sigma bonds come in six varieties: Pi bonds come in one
- A Key Skill: How to Calculate Formal Charge
- The Four Intermolecular Forces and How They Affect Boiling Points
- 3 Trends That Affect Boiling Points
- How To Use Electronegativity To Determine Electron Density (and why NOT to trust formal charge)
- Introduction to Resonance
- How To Use Curved Arrows To Interchange Resonance Forms
- Evaluating Resonance Forms (1) - The Rule of Least Charges
- How To Find The Best Resonance Structure By Applying Electronegativity
- Evaluating Resonance Structures With Negative Charges
- Evaluating Resonance Structures With Positive Charge
- Exploring Resonance: Pi-Donation
- Exploring Resonance: Pi-acceptors
- In Summary: Evaluating Resonance Structures
- Drawing Resonance Structures: 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid
- How to apply electronegativity and resonance to understand reactivity
- Bond Hybridization Practice
- Structure and Bonding Practice Quizzes
- Resonance Structures Practice
02 Acid Base Reactions
- Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid Base Reactions In Organic Chemistry
- The Stronger The Acid, The Weaker The Conjugate Base
- Walkthrough of Acid-Base Reactions (3) - Acidity Trends
- Five Key Factors That Influence Acidity
- Acid-Base Reactions: Introducing Ka and pKa
- How to Use a pKa Table
- The pKa Table Is Your Friend
- A Handy Rule of Thumb for Acid-Base Reactions
- Acid Base Reactions Are Fast
- pKa Values Span 60 Orders Of Magnitude
- How Protonation and Deprotonation Affect Reactivity
- Acid Base Practice Problems
03 Alkanes and Nomenclature
- Meet the (Most Important) Functional Groups
- Condensed Formulas: Deciphering What the Brackets Mean
- Hidden Hydrogens, Hidden Lone Pairs, Hidden Counterions
- Don't Be Futyl, Learn The Butyls
- Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, Quaternary In Organic Chemistry
- Branching, and Its Affect On Melting and Boiling Points
- The Many, Many Ways of Drawing Butane
- Wedge And Dash Convention For Tetrahedral Carbon
- Common Mistakes in Organic Chemistry: Pentavalent Carbon
- Table of Functional Group Priorities for Nomenclature
- Summary Sheet - Alkane Nomenclature
- Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature Demystified With A Simple Puzzle Piece Approach
- Boiling Point Quizzes
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Quizzes
04 Conformations and Cycloalkanes
- Staggered vs Eclipsed Conformations of Ethane
- Conformational Isomers of Propane
- Newman Projection of Butane (and Gauche Conformation)
- Introduction to Cycloalkanes
- Geometric Isomers In Small Rings: Cis And Trans Cycloalkanes
- Calculation of Ring Strain In Cycloalkanes
- Cycloalkanes - Ring Strain In Cyclopropane And Cyclobutane
- Cyclohexane Conformations
- Cyclohexane Chair Conformation: An Aerial Tour
- How To Draw The Cyclohexane Chair Conformation
- The Cyclohexane Chair Flip
- The Cyclohexane Chair Flip - Energy Diagram
- Substituted Cyclohexanes - Axial vs Equatorial
- Ranking The Bulkiness Of Substituents On Cyclohexanes: "A-Values"
- Cyclohexane Chair Conformation Stability: Which One Is Lower Energy?
- Fused Rings - Cis-Decalin and Trans-Decalin
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds - Fused, Bridged, and Spiro
- Bredt's Rule (And Summary of Cycloalkanes)
- Newman Projection Practice
- Cycloalkanes Practice Problems
05 A Primer On Organic Reactions
- The Most Important Question To Ask When Learning a New Reaction
- Curved Arrows (for reactions)
- Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- The Three Classes of Nucleophiles
- Nucleophilicity vs. Basicity
- What Makes A Good Nucleophile?
- What Makes A Good Leaving Group?
- 3 Factors That Stabilize Carbocations
- Equilibrium and Energy Relationships
- 7 Factors that stabilize negative charge in organic chemistry
- 7 Factors That Stabilize Positive Charge in Organic Chemistry
- What's a Transition State?
- Hammond's Postulate
- Learning Organic Chemistry Reactions: A Checklist (PDF)
- Introduction to Oxidative Cleavage Reactions
06 Free Radical Reactions
- Bond Dissociation Energies = Homolytic Cleavage
- Free Radical Reactions
- 3 Factors That Stabilize Free Radicals
- What Factors Destabilize Free Radicals?
- Bond Strengths And Radical Stability
- Free Radical Initiation: Why Is "Light" Or "Heat" Required?
- Initiation, Propagation, Termination
- Monochlorination Products Of Propane, Pentane, And Other Alkanes
- Selectivity In Free Radical Reactions
- Selectivity in Free Radical Reactions: Bromination vs. Chlorination
- Halogenation At Tiffany's
- Allylic Bromination
- Bonus Topic: Allylic Rearrangements
- In Summary: Free Radicals
- Synthesis (2) - Reactions of Alkanes
- Free Radicals Practice Quizzes
07 Stereochemistry and Chirality
- Types of Isomers: Constitutional Isomers, Stereoisomers, Enantiomers, and Diastereomers
- How To Draw The Enantiomer Of A Chiral Molecule
- How To Draw A Bond Rotation
- Introduction to Assigning (R) and (S): The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Rules
- Assigning Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) Priorities (2) - The Method of Dots
- Enantiomers vs Diastereomers vs The Same? Two Methods For Solving Problems
- Assigning R/S To Newman Projections (And Converting Newman To Line Diagrams)
- How To Determine R and S Configurations On A Fischer Projection
- The Meso Trap
- Optical Rotation, Optical Activity, and Specific Rotation
- Optical Purity and Enantiomeric Excess
- What's a Racemic Mixture?
- Chiral Allenes And Chiral Axes
- Stereochemistry Practice Problems and Quizzes
08 Substitution Reactions
- Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions - Introduction
- Two Types of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
- The SN2 Mechanism
- Why the SN2 Reaction Is Powerful
- The SN1 Mechanism
- The Conjugate Acid Is A Better Leaving Group
- Comparing the SN1 and SN2 Reactions
- Polar Protic? Polar Aprotic? Nonpolar? All About Solvents
- Steric Hindrance is Like a Fat Goalie
- Common Blind Spot: Intramolecular Reactions
- Substitution Practice - SN1
- Substitution Practice - SN2
09 Elimination Reactions
- Elimination Reactions (1): Introduction And The Key Pattern
- Elimination Reactions (2): The Zaitsev Rule
- Elimination Reactions Are Favored By Heat
- Two Elimination Reaction Patterns
- The E1 Reaction
- The E2 Mechanism
- E1 vs E2: Comparing the E1 and E2 Reactions
- Antiperiplanar Relationships: The E2 Reaction and Cyclohexane Rings
- Bulky Bases in Elimination Reactions
- Comparing the E1 vs SN1 Reactions
- Elimination (E1) Reactions With Rearrangements
- E1cB - Elimination (Unimolecular) Conjugate Base
- Elimination (E1) Practice Problems And Solutions
- Elimination (E2) Practice Problems and Solutions
10 Rearrangements
11 SN1/SN2/E1/E2 Decision
- Identifying Where Substitution and Elimination Reactions Happen
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (1) - The Substrate
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 (2) - The Nucleophile/Base
- SN1 vs E1 and SN2 vs E2 : The Temperature
- Deciding SN1/SN2/E1/E2 - The Solvent
- Wrapup: The Key Factors For Determining SN1/SN2/E1/E2
- Alkyl Halide Reaction Map And Summary
- SN1 SN2 E1 E2 Practice Problems
12 Alkene Reactions
- E and Z Notation For Alkenes (+ Cis/Trans)
- Alkene Stability
- Alkene Addition Reactions: "Regioselectivity" and "Stereoselectivity" (Syn/Anti)
- Stereoselective and Stereospecific Reactions
- Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes and Markovnikov's Rule
- Hydration of Alkenes With Aqueous Acid
- Rearrangements in Alkene Addition Reactions
- Halogenation of Alkenes and Halohydrin Formation
- Oxymercuration Demercuration of Alkenes
- Hydroboration Oxidation of Alkenes
- m-CPBA (meta-chloroperoxybenzoic acid)
- OsO4 (Osmium Tetroxide) for Dihydroxylation of Alkenes
- Palladium on Carbon (Pd/C) for Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes
- Cyclopropanation of Alkenes
- A Fourth Alkene Addition Pattern - Free Radical Addition
- Alkene Reactions: Ozonolysis
- Summary: Three Key Families Of Alkene Reaction Mechanisms
- Synthesis (4) - Alkene Reaction Map, Including Alkyl Halide Reactions
- Alkene Reactions Practice Problems
13 Alkyne Reactions
- Acetylides from Alkynes, And Substitution Reactions of Acetylides
- Partial Reduction of Alkynes With Lindlar's Catalyst
- Partial Reduction of Alkynes With Na/NH3 To Obtain Trans Alkenes
- Alkyne Hydroboration With "R2BH"
- Hydration and Oxymercuration of Alkynes
- Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
- Alkyne Halogenation: Bromination and Chlorination of Alkynes
- Alkyne Reactions - The "Concerted" Pathway
- Alkenes To Alkynes Via Halogenation And Elimination Reactions
- Alkynes Are A Blank Canvas
- Synthesis (5) - Reactions of Alkynes
- Alkyne Reactions Practice Problems With Answers
14 Alcohols, Epoxides and Ethers
- Alcohols - Nomenclature and Properties
- Alcohols Can Act As Acids Or Bases (And Why It Matters)
- Alcohols - Acidity and Basicity
- The Williamson Ether Synthesis
- Ethers From Alkenes, Tertiary Alkyl Halides and Alkoxymercuration
- Alcohols To Ethers via Acid Catalysis
- Cleavage Of Ethers With Acid
- Epoxides - The Outlier Of The Ether Family
- Opening of Epoxides With Acid
- Epoxide Ring Opening With Base
- Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols
- Tosylates And Mesylates
- PBr3 and SOCl2
- Elimination Reactions of Alcohols
- Elimination of Alcohols To Alkenes With POCl3
- Alcohol Oxidation: "Strong" and "Weak" Oxidants
- Demystifying The Mechanisms of Alcohol Oxidations
- Protecting Groups For Alcohols
- Thiols And Thioethers
- Calculating the oxidation state of a carbon
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Oxidation Ladders
- SOCl2 Mechanism For Alcohols To Alkyl Halides: SN2 versus SNi
- Alcohol Reactions Roadmap (PDF)
- Alcohol Reaction Practice Problems
- Epoxide Reaction Quizzes
- Oxidation and Reduction Practice Quizzes
15 Organometallics
- What's An Organometallic?
- Formation of Grignard and Organolithium Reagents
- Organometallics Are Strong Bases
- Reactions of Grignard Reagents
- Protecting Groups In Grignard Reactions
- Synthesis Problems Involving Grignard Reagents
- Grignard Reactions And Synthesis (2)
- Organocuprates (Gilman Reagents): How They're Made
- Gilman Reagents (Organocuprates): What They're Used For
- The Heck, Suzuki, and Olefin Metathesis Reactions (And Why They Don't Belong In Most Introductory Organic Chemistry Courses)
- Reaction Map: Reactions of Organometallics
- Grignard Practice Problems
16 Spectroscopy
- Degrees of Unsaturation (or IHD, Index of Hydrogen Deficiency)
- Conjugation And Color (+ How Bleach Works)
- Introduction To UV-Vis Spectroscopy
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Absorbance of Carbonyls
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy: Practice Questions
- Bond Vibrations, Infrared Spectroscopy, and the "Ball and Spring" Model
- Infrared Spectroscopy: A Quick Primer On Interpreting Spectra
- IR Spectroscopy: 4 Practice Problems
- 1H NMR: How Many Signals?
- Homotopic, Enantiotopic, Diastereotopic
- Diastereotopic Protons in 1H NMR Spectroscopy: Examples
- 13-C NMR - How Many Signals
- Liquid Gold: Pheromones In Doe Urine
- Natural Product Isolation (1) - Extraction
- Natural Product Isolation (2) - Purification Techniques, An Overview
- Structure Determination Case Study: Deer Tarsal Gland Pheromone
17 Dienes and MO Theory
- What To Expect In Organic Chemistry 2
- Are these molecules conjugated?
- Conjugation And Resonance In Organic Chemistry
- Bonding And Antibonding Pi Orbitals
- Molecular Orbitals of The Allyl Cation, Allyl Radical, and Allyl Anion
- Pi Molecular Orbitals of Butadiene
- Reactions of Dienes: 1,2 and 1,4 Addition
- Thermodynamic and Kinetic Products
- More On 1,2 and 1,4 Additions To Dienes
- s-cis and s-trans
- The Diels-Alder Reaction
- Cyclic Dienes and Dienophiles in the Diels-Alder Reaction
- Stereochemistry of the Diels-Alder Reaction
- Exo vs Endo Products In The Diels Alder: How To Tell Them Apart
- HOMO and LUMO In the Diels Alder Reaction
- Why Are Endo vs Exo Products Favored in the Diels-Alder Reaction?
- Diels-Alder Reaction: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control
- The Retro Diels-Alder Reaction
- The Intramolecular Diels Alder Reaction
- Regiochemistry In The Diels-Alder Reaction
- The Cope and Claisen Rearrangements
- Electrocyclic Reactions
- Electrocyclic Ring Opening And Closure (2) - Six (or Eight) Pi Electrons
- Diels Alder Practice Problems
- Molecular Orbital Theory Practice
18 Aromaticity
- Introduction To Aromaticity
- Rules For Aromaticity
- Huckel's Rule: What Does 4n+2 Mean?
- Aromatic, Non-Aromatic, or Antiaromatic? Some Practice Problems
- Antiaromatic Compounds and Antiaromaticity
- The Pi Molecular Orbitals of Benzene
- The Pi Molecular Orbitals of Cyclobutadiene
- Frost Circles
- Aromaticity Practice Quizzes
19 Reactions of Aromatic Molecules
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Introduction
- Activating and Deactivating Groups In Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution - The Mechanism
- Ortho-, Para- and Meta- Directors in Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- Understanding Ortho, Para, and Meta Directors
- Why are halogens ortho- para- directors?
- Disubstituted Benzenes: The Strongest Electron-Donor "Wins"
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions (1) - Halogenation of Benzene
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitutions (2) - Nitration and Sulfonation
- EAS Reactions (3) - Friedel-Crafts Acylation and Friedel-Crafts Alkylation
- Intramolecular Friedel-Crafts Reactions
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (NAS)
- Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution (2) - The Benzyne Mechanism
- Reactions on the "Benzylic" Carbon: Bromination And Oxidation
- The Wolff-Kishner, Clemmensen, And Other Carbonyl Reductions
- More Reactions on the Aromatic Sidechain: Reduction of Nitro Groups and the Baeyer Villiger
- Aromatic Synthesis (1) - "Order Of Operations"
- Synthesis of Benzene Derivatives (2) - Polarity Reversal
- Aromatic Synthesis (3) - Sulfonyl Blocking Groups
- Birch Reduction
- Synthesis (7): Reaction Map of Benzene and Related Aromatic Compounds
- Aromatic Reactions and Synthesis Practice
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Practice Problems
20 Aldehydes and Ketones
- What's The Alpha Carbon In Carbonyl Compounds?
- Nucleophilic Addition To Carbonyls
- Aldehydes and Ketones: 14 Reactions With The Same Mechanism
- Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4) Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones
- Grignard Reagents For Addition To Aldehydes and Ketones
- Wittig Reaction
- Hydrates, Hemiacetals, and Acetals
- Imines - Properties, Formation, Reactions, and Mechanisms
- All About Enamines
- Breaking Down Carbonyl Reaction Mechanisms: Reactions of Anionic Nucleophiles (Part 2)
- Aldehydes Ketones Reaction Practice
21 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution (With Negatively Charged Nucleophiles)
- Addition-Elimination Mechanisms With Neutral Nucleophiles (Including Acid Catalysis)
- Basic Hydrolysis of Esters - Saponification
- Transesterification
- Proton Transfer
- Fischer Esterification - Carboxylic Acid to Ester Under Acidic Conditions
- Lithium Aluminum Hydride (LiAlH4) For Reduction of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
- LiAlH[Ot-Bu]3 For The Reduction of Acid Halides To Aldehydes
- Di-isobutyl Aluminum Hydride (DIBAL) For The Partial Reduction of Esters and Nitriles
- Amide Hydrolysis
- Thionyl Chloride (SOCl2) And Conversion of Carboxylic Acids to Acid Halides
- Diazomethane (CH2N2)
- Carbonyl Chemistry: Learn Six Mechanisms For the Price Of One
- Making Music With Mechanisms (PADPED)
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Practice Questions
22 Enols and Enolates
- Keto-Enol Tautomerism
- Enolates - Formation, Stability, and Simple Reactions
- Kinetic Versus Thermodynamic Enolates
- Aldol Addition and Condensation Reactions
- Reactions of Enols - Acid-Catalyzed Aldol, Halogenation, and Mannich Reactions
- Claisen Condensation and Dieckmann Condensation
- Decarboxylation
- The Malonic Ester and Acetoacetic Ester Synthesis
- The Michael Addition Reaction and Conjugate Addition
- The Robinson Annulation
- Haloform Reaction
- The Hell–Volhard–Zelinsky Reaction
- Enols and Enolates Practice Quizzes
23 Amines
- The Amide Functional Group: Properties, Synthesis, and Nomenclature
- Basicity of Amines And pKaH
- 5 Key Basicity Trends of Amines
- The Mesomeric Effect And Aromatic Amines
- Nucleophilicity of Amines
- Alkylation of Amines (Sucks!)
- Reductive Amination
- The Gabriel Synthesis
- Some Reactions of Azides
- The Hofmann Elimination
- The Hofmann and Curtius Rearrangements
- The Cope Elimination
- Protecting Groups for Amines - Carbamates
- The Strecker Synthesis of Amino Acids
- Introduction to Peptide Synthesis
- Reactions of Diazonium Salts: Sandmeyer and Related Reactions
- Amine Practice Questions
24 Carbohydrates
- D and L Notation For Sugars
- Pyranoses and Furanoses: Ring-Chain Tautomerism In Sugars
- What is Mutarotation?
- Reducing Sugars
- The Big Damn Post Of Carbohydrate-Related Chemistry Definitions
- The Haworth Projection
- Converting a Fischer Projection To A Haworth (And Vice Versa)
- Reactions of Sugars: Glycosylation and Protection
- The Ruff Degradation and Kiliani-Fischer Synthesis
- Isoelectric Points of Amino Acids (and How To Calculate Them)
- Carbohydrates Practice
- Amino Acid Quizzes
25 Fun and Miscellaneous
- A Gallery of Some Interesting Molecules From Nature
- Screw Organic Chemistry, I'm Just Going To Write About Cats
- On Cats, Part 1: Conformations and Configurations
- On Cats, Part 2: Cat Line Diagrams
- On Cats, Part 4: Enantiocats
- On Cats, Part 6: Stereocenters
- Organic Chemistry Is Shit
- The Organic Chemistry Behind "The Pill"
- Maybe they should call them, "Formal Wins" ?
- Why Do Organic Chemists Use Kilocalories?
- The Principle of Least Effort
- Organic Chemistry GIFS - Resonance Forms
- Reproducibility In Organic Chemistry
- What Holds The Nucleus Together?
- How Reactions Are Like Music
- Organic Chemistry and the New MCAT
26 Organic Chemistry Tips and Tricks
- Common Mistakes: Formal Charges Can Mislead
- Partial Charges Give Clues About Electron Flow
- Draw The Ugly Version First
- Organic Chemistry Study Tips: Learn the Trends
- The 8 Types of Arrows In Organic Chemistry, Explained
- Top 10 Skills To Master Before An Organic Chemistry 2 Final
- Common Mistakes with Carbonyls: Carboxylic Acids... Are Acids!
- Planning Organic Synthesis With "Reaction Maps"
- Alkene Addition Pattern #1: The "Carbocation Pathway"
- Alkene Addition Pattern #2: The "Three-Membered Ring" Pathway
- Alkene Addition Pattern #3: The "Concerted" Pathway
- Number Your Carbons!
- The 4 Major Classes of Reactions in Org 1
- How (and why) electrons flow
- Grossman's Rule
- Three Exam Tips
- A 3-Step Method For Thinking Through Synthesis Problems
- Putting It Together
- Putting Diels-Alder Products in Perspective
- The Ups and Downs of Cyclohexanes
- The Most Annoying Exceptions in Org 1 (Part 1)
- The Most Annoying Exceptions in Org 1 (Part 2)
- The Marriage May Be Bad, But the Divorce Still Costs Money
- 9 Nomenclature Conventions To Know
- Nucleophile attacks Electrophile
27 Case Studies of Successful O-Chem Students
- Success Stories: How Corina Got The The "Hard" Professor - And Got An A+ Anyway
- How Helena Aced Organic Chemistry
- From a "Drop" To B+ in Org 2 – How A Hard Working Student Turned It Around
- How Serge Aced Organic Chemistry
- Success Stories: How Zach Aced Organic Chemistry 1
- Success Stories: How Kari Went From C– to B+
- How Esther Bounced Back From a "C" To Get A's In Organic Chemistry 1 And 2
- How Tyrell Got The Highest Grade In Her Organic Chemistry Course
- This Is Why Students Use Flashcards
- Success Stories: How Stu Aced Organic Chemistry
- How John Pulled Up His Organic Chemistry Exam Grades
- Success Stories: How Nathan Aced Organic Chemistry (Without It Taking Over His Life)
- How Chris Aced Org 1 and Org 2
- Interview: How Jay Got an A+ In Organic Chemistry
- How to Do Well in Organic Chemistry: One Student's Advice
- "America's Top TA" Shares His Secrets For Teaching O-Chem
- "Organic Chemistry Is Like..." - A Few Metaphors
- How To Do Well In Organic Chemistry: Advice From A Tutor
- Guest post: "I went from being afraid of tests to actually looking forward to them".
Thank you !
I am a retired chemistry instructor now volunteering as a tutor at a small liberal arts college. How small? About 700 students. We have excellent chemistry instructors but Organic Chem is a challenge to even the best students. I like this website because before I read it I had been telling the students they would need to memorize about 625 type reactions as I did at the end of my junior year when I was preparing for the NSTA-Acs exam. Your site is very helpful. Thank you.
Edit: decided to go with ionic bond forming/breaking, don’t want to cause any confusion.
I do the same thing, James! Though I leave out acid/base reactions and use the line “almost all reactions in this course are either acid/base reactions or one of the following three…” as they learn acid/base reactions in freshman chemistry.
You should also check out this paper too: J. Chem. Educ., 2008, 85 (1), p 83. Great, readable paper I give out to my students just at the end of the term to facilitate their studying. If you give it out at the beginning, they won’t understand it and won’t read it.
This one? :-) https://masterorganicchemistry.com/2010/08/25/the-six-pillars-of-organic-chemistry/
I shoulda known you’d have read that paper. Yeesh.
Well, it was a great paper. Thanks for making me aware of it!
You’re right- I wanted to make it clearer for people to be able to see which bonds are forming and breaking, even if normally “ionic” bonds are drawn as covalent bonds. This is something you’ll see quite a bit of in textbooks, by the way – ionic bonds are commonly drawn as covalent, just to avoid drawing in the partial charges. You’re just supposed to “know” by later chapters that these bonds are ionic.
I actually like the way you drew the first reaction, James, because the reaction is balanced. As a student, missing counterions in multi-step mechanisms used to drive me crazy (and still do)…
Dig the new site design!
Missing counterions drove/drive me nuts too. I am glad I’m not the only person who feels this way. How are you supposed to understand what’s going on if you’re not told half the story? I am going to write an angry rant about this.
Glad the new design works for you… it was time!
It’s kinda strange in your first case that you show a covalent bond forming between sulfur and sodium. It’s also strange that you show Na-OH instead of NaOH- same goes for the sodium ethoxide and NaCN.